109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

HMGB1 siRNA 在体内体外减轻高糖环境下视网膜细胞损害的实验研究
Authors Jiang S, Chen X
Received 10 December 2016
Accepted for publication 22 January 2017
Published 15 March 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 783—795
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S129913
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Dragan Hrncic
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Background: Diabetic retinopathy (DR), one of the most common complications of
late-phase diabetes, is associated with many risk factors, among which
continuous low-grade inflammation is one of the principal ones. As such,
lowering inflammation levels and maintain the viability of human retinal
endothelial cells (HRECs) are critical for DR therapy. HMGB1 is a well-known
proinflammatory cytokine. However, whether HMGB1 small interfering RNA (siRNA)
can protect retina cells under a high-glucose environment from morphological
changes and functional abnormalities remain undetermined. We aimed to
investigate the effect of HMGB1 siRNA on retinal cells in DR.
Materials and methods: A total of 80 adult Wistar rats were randomly divided
into four groups (n=20 each): normal control, diabetes mellitus (DM), scrambled
(Scr) siRNA, and HMGB1 siRNA. Rats in the DM, Scr siRNA, and siRNA groups were
established by intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin. At 16 weeks after
injection, rats in the siRNA and Scr-siRNA groups were intravitreally injected
with 2 µL HMGB1 siRNA and 2 µL Scr-siRNA, while rats in the control and DM
groups were intravitreally injected with the same dose of sterile saline. At 1
week after injections, we performed the following experiments. Immunohistochemical
staining and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction were performed to
test HMGB1 protein and messenger RNA expression in retinas. We performed TUNEL
assays to detect retinal cell apoptosis and electroretinography to detect
retinal function. In HRECs treated with high glucose, proliferation,
morphology, apoptosis, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and reactive oxygen species
production were detected. Western blot was applied to determine the expressions
of HMGB1 and its related protein and apoptosis protein.
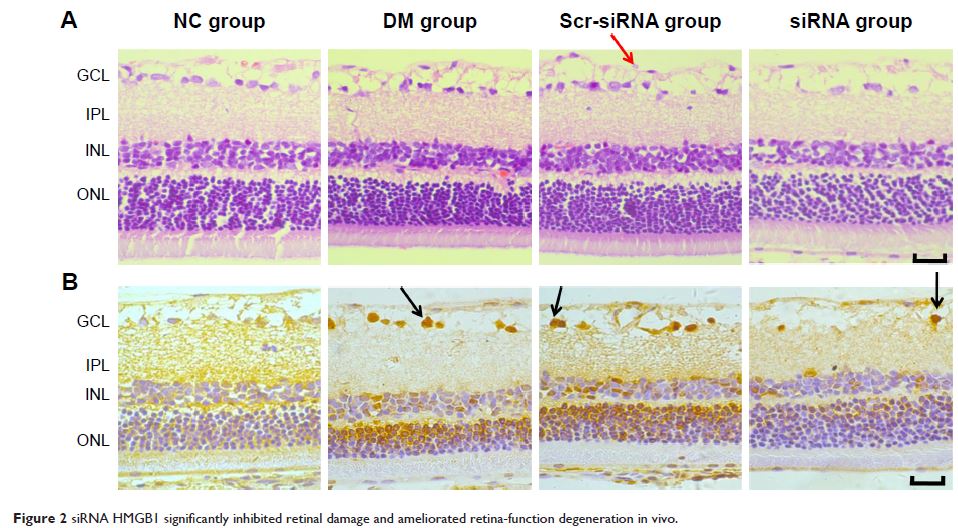
Results: Intravitreal injection of HMGB1 siRNA reduced protein
and messenger RNA expression of HMGB1 (both P <0.05). Intravitreal injection
of HMGB1 siRNA reduced apoptosis of retinal cells (P <0.05),
protected morphological changes in the retina, and improved the function of the
retina (P <0.05). In HRECs treated with
high glucose, HMGB1 siRNA pretreatment increased cell viability, reduced cell
apoptosis, and reduced oxidative damage to cells (all P <0.05). Western
blot detection found that HMGB1 siRNA pretreatment can inhibit the expression
of cleaved caspase 3 and improve the expression of BCL2 (P <0.05). HMGB1 and NFκB
expression increased in a time-dependent manner in the high-glucose environment
and IKKβ and NFκB protein expression decreased significantly after HMGB1
silencing.
Conclusion: As a therapeutic target, HMGB1 siRNA can reduce
retinal cell damage induced by high glucose in vitro and in vivo and delay DR
progress through the HMGB1–IKKβ–NFκB signaling pathway.
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy, small
interfering RNA, human retinal endothelial cells, high-mobility group box 1,
inhibitor of nuclear factor κB, nuclear factor κB