109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

辛酰基半乳糖酯 (Octanoyl galactose ester) 改性微乳液系统通过薏苡仁 (coix seed) 组分自组装以增强肿瘤靶向和加强肝癌治疗
Authors Qu D, Liu M, Huang M, Wang L, Chen Y, Liu C, Liu Y
Received 20 October 2016
Accepted for publication 27 December 2016
Published 14 March 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2045—2059
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S125293
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
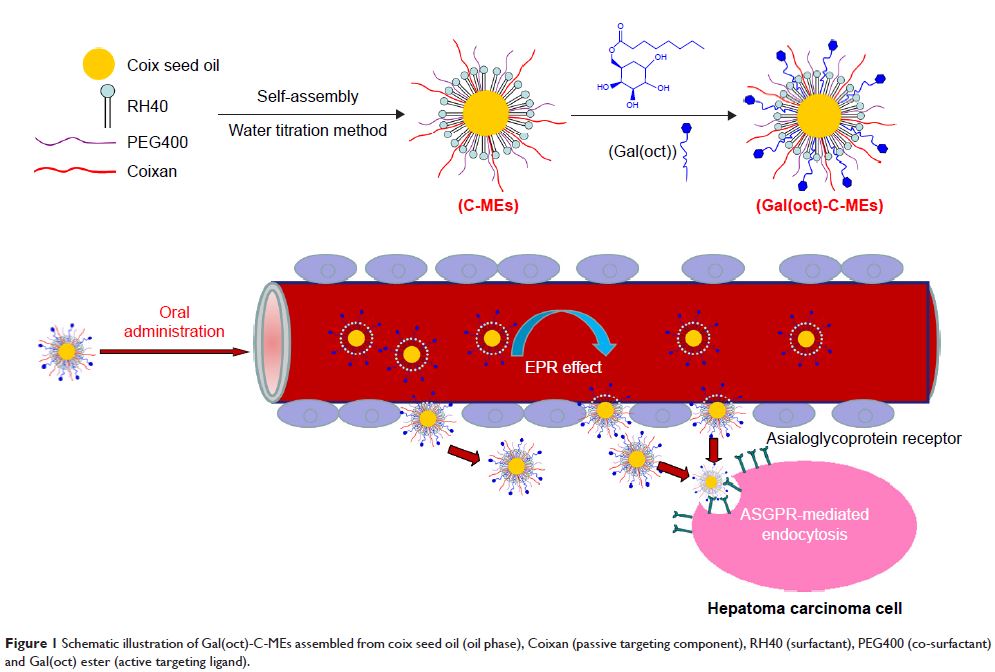
Abstract: A nanosized drug delivery platform with a combination of rational
components and tumor targeting is significant for enhancement of anticancer
therapy and reduction of side effects. In this study, we developed a octanoyl
galactose ester-modified microemulsion system self-assembled by coix seed components
(Gal(oct)-C-MEs), which improved the tumor accumulation through
asialoglycoprotein receptor-mediated endocytosis and promoted the antitumor
efficacy through multicomponent-mediated synergistic effect. Octanoyl galactose
ester (Gal(oct)) with a yield of 82.3% was synthesized through a green
enzymatic reaction and multidimensional characterization. Gal(oct)-C-MEs with a
spherical shape had a small and uniform particle size (58.49±1.03 nm), narrow
polydispersity index (0.09±0.01) and neutral surface charge (-5.82±0.57 mV). In
the cellular uptake studies, the internalized Gal(oct)-C-ME was 2.28-fold
higher relative to that of coix seed component-based microemulsions (C-MEs).
The half-maximal inhibitory concentration of Gal(oct)-C-MEs against HepG2 cells
was 46.5±2.4 µg/mL, which was notably higher than that of C-MEs. Importantly,
the intratumor fluorescence of HepG2 xenograft-bearing nude mice treated with
Cy5/Gal(oct)-C-MEs was 1.9-fold higher relative to treatment with Cy5/C-MEs. In
the study of antitumor efficacy in vivo, HepG2 xenograft-bearing nude mice
intragastrically administered Gal(oct)-C-MEs for 14 days exhibited the
strongest inhibition of tumor growth and the lowest toxicity against liver and
kidney among all the treatments. In summary, Gal(oct)-C-ME, as a highly
effective and safe anticancer drug delivery system, showed promising potential
for hepatoma therapy.
Keywords: coix seed oil, coixan,
multicomponent-based microemulsion, hepatic targeting, antihepatoma, oral drug
delivery system