109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
将肽样抑制剂作为生物受体,基于金纳米粒子的电化学方法可用于检测蛋白激酶
Authors Sun K, Chang Y, Zhou B, Wang X, Liu L
Received 17 November 2016
Accepted for publication 18 January 2017
Published 9 March 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1905—1915
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S127957
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
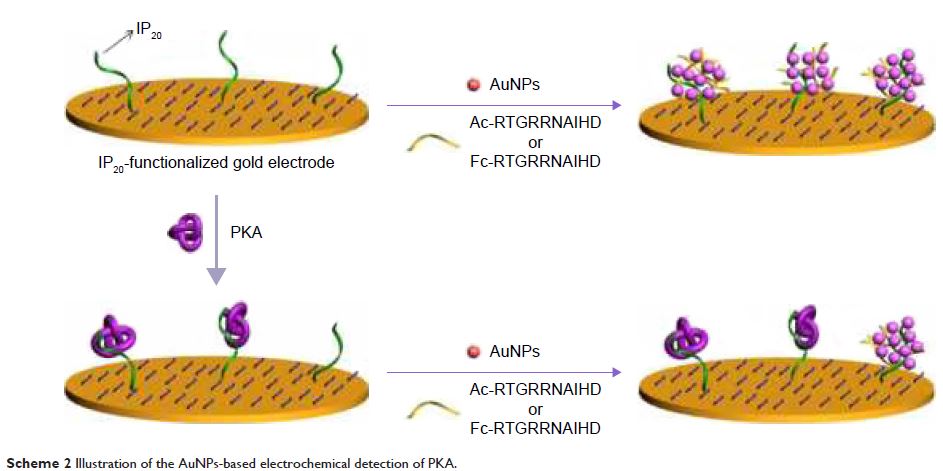
Abstract: This article presents
a general method for the detection of protein kinase with a peptide-like kinase
inhibitor as the bioreceptor, and it was done by converting gold nanoparticles
(AuNPs)-based colorimetric assay into sensitive electrochemical analysis. In
the colorimetric assay, the kinase-specific aptameric peptide triggered the aggregation
of AuNPs in solution. However, the specific binding of peptide to the target
protein (kinase) inhibited its ability to trigger the assembly of AuNPs. In the
electrochemical analysis, peptides immobilized on a gold electrode and
presented as solution triggered together the in situ formation of AuNPs-based
network architecture on the electrode surface. Nevertheless, the formation of
peptide–kinase complex on the electrode surface made the peptide-triggered
AuNPs assembly difficult. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was used to
measure the change in surface property in the binding events. When a
ferrocene-labeled peptide (Fc-peptide) was used in this design, the network of
AuNPs/Fc-peptide produced a good voltammetric signal. The competitive assay allowed
for the detection of protein kinase A with a detection limit of 20 mU/mL. This
work should be valuable for designing novel optical or electronic biosensors
and likely lead to many detection applications.
Keywords: electrochemical biosensor, colorimetric assay, gold nanoparticle, aptameric peptide, protein kinase A, signal amplification
Keywords: electrochemical biosensor, colorimetric assay, gold nanoparticle, aptameric peptide, protein kinase A, signal amplification