109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
使用还原敏感的脂质 - 聚合物杂合纳米颗粒进行多柔比星 (Doxorubicin) 和雷公藤 (triptolide) 内酯共同递送,用于体外和体内协同癌症治疗
Authors Wu B, Lu S, Zhang L, Zhuo RX, Xu HB, Huang SW
Received 28 December 2016
Accepted for publication 13 February 2017
Published 8 March 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1853—1862
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S131235
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jiang Yang
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Codelivery is a
promising strategy to overcome the limitations of single chemotherapeutic
agents in cancer treatment. Despite progress, codelivery of two or more
different functional drugs to increase anticancer efficiency still remains a
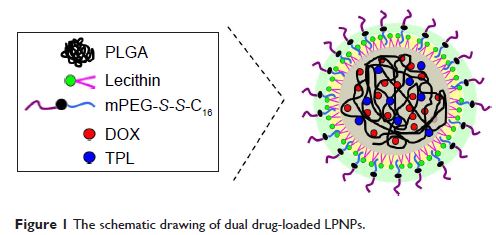
challenge. Here, reduction-sensitive lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPNPs)
drug delivery system composed of monomethoxy-poly(ethylene glycol)-S -S -hexadecyl
(mPEG-S -S -C16), soybean lecithin, and
poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) was used for codelivery of doxorubicin
(DOX) and a Chinese herb extract triptolide (TPL). Hydrophobic DOX and TPL
could be successfully loaded in LPNPs by self-assembly. More importantly, drug
release and cellular uptake experiments demonstrated that the two drugs were
reduction sensitive, released simultaneously from LPNPs, and taken up
effectively by the tumor cells. DOX/TPL-coloaded LPNPs (DOX/TPL-LPNPs)
exhibited a high level of synergistic activation with low combination index
(CI) in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, the highest synergistic therapeutic effect
was achieved at the ratio of 1:0.2 DOX/TPL. Further experiments showed that TPL
enhanced the uptake of DOX by human oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma cells
(KB cells). Overall, DOX/TPL-coencapsulated reduction-sensitive nanoparticles
will be a promising strategy for cancer treatment.
Keywords: triptolide, codelivery, reduction sensitive, synergistic effect
Keywords: triptolide, codelivery, reduction sensitive, synergistic effect