109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用加载 pH 响应性聚合物涂覆药物的黑色素样纳米颗粒的高效光热化学治疗
Authors Zhang C, Zhao X, Guo S, Lin T, Guo H
Received 17 December 2016
Accepted for publication 13 February 2017
Published 7 March 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1827—1840
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S130539
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
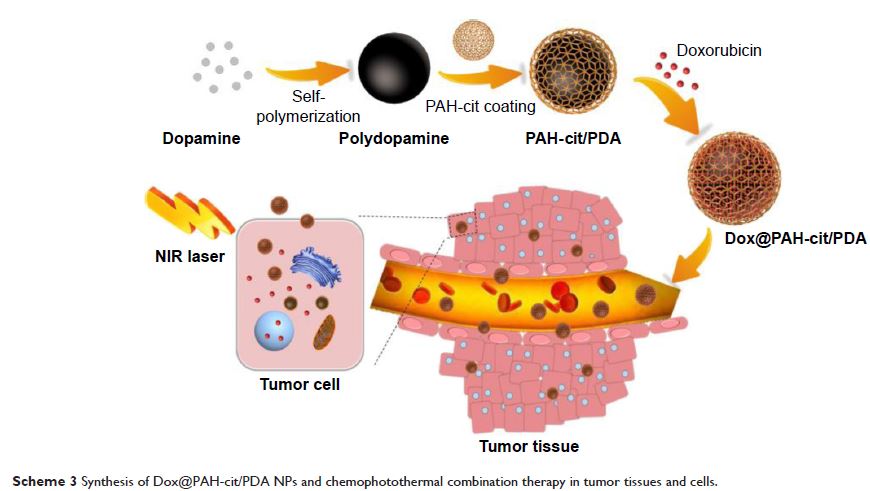
Abstract: Dopamine is a neurotransmitter commonly used in clinical treatment.
Polydopamine (PDA) has excellent histocompatibility and biosafety and can
efficiently convert near-infrared reflection (NIR) to thermal energy. In this
study, PDA was used as a promising carrier, and pH-responsive polymer-coated drug-loaded
PDA nanoparticles (NPs; doxorubicin@poly(allylamine)-citraconic anhydride
[Dox@PAH-cit]/PDA NPs) were developed. As expected, the Dox@PAH-cit/PDA NPs
exhibited excellent photothermal efficiency. In addition, at a low pH
condition, the loaded Dox was released from the NPs due to the amide hydrolysis
of PAH-cit. Upon NIR exposure (808 nm), the temperature of the NP solution
rapidly increases to kill tumor cells. Compared with unbound chemotherapy
drugs, the NPs have a stronger cell uptake ability. In vivo, the PDA NPs were
able to efficiently accumulate at the tumor location. After intravenous
administration and NIR exposure, tumor growth was significantly inhibited. In
summary, the present investigation demonstrated that the Dox@PAH-cit/PDA NPs
presented highly effective photothermal chemotherapy for prostate cancer.
Keywords: prostate cancer, photothermal therapy,
near-infrared reflection, dopamine, PAH-cit, drug delivery