109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对中国卒中幸存者卒中后抑郁症的各种亚型的新观点
Authors Yue Y, Liu R, Cao Y, Wu Y, Zhang S, Li H, Zhu J, Jiang W, Wu A, Yuan Y
Received 22 November 2016
Accepted for publication 13 January 2017
Published 6 March 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 707—713
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S128429
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
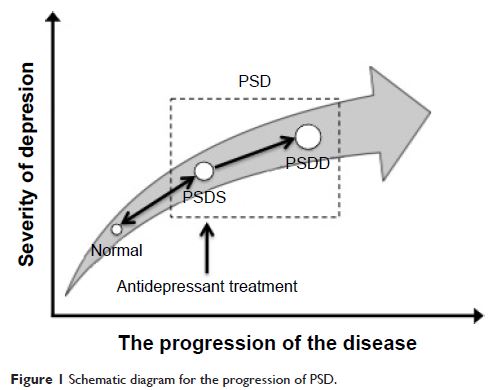
Aim: Poststroke depression (PSD) is the most common complication of stroke.
However, some stroke survivors with depression cannot meet the diagnostic
criteria of PSD. The aim of this study was to propose the new conception of
stroke patients with depression and then make them to receive reasonable
diagnosis and treatment.
Methods: We first put forward the opinion that the general PSD
should consist of PSD disorder (PSDD) and PSD symptoms (PSDS) according to the Diagnostic and Statistical
Manual of Mental Disorder –
Fifth Edition (DSM-5) and ZhongDa diagnostic criteria – first edition (ZD-1),
respectively. The ZD-1 was established based on the suggestions of
65 Chinese chief doctors considering that the symptoms of PSDS might be
different from those of PSDD and the duration of DSM-5 was too strict. Then,
166 stroke inpatients were recruited, and the study was conducted using the
diagnosis and classification of PSD to verify the new concept.
Results: A total of 24 (14.46%) and 80 (48.19%) stroke patients
were diagnosed with PSDD and PSDS, respectively, according to individual
diagnosis criteria. Moreover, patients meeting the diagnostic criteria of PSDD
should satisfy the criteria of PSDS first. The distribution frequencies of
depressive symptoms were different, which suggested that there might be
discrepant depressive symptoms between PSDS and PSDD.
Conclusion: The present study proposes new opinion about the
classification and diagnosis of depression in stroke survivors. The definition
and criteria of PSDS are beneficial to explore phenomenological consistency and
provide useful information for early recognition and appropriate interventions.
Keywords: poststroke depression, subtypes,
diagnostic criteria