109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

加载紫杉醇 (Paclitaxel) 的星形共聚物纳米粒子用于恶性黑素瘤的强化化疗以克服多药耐药性
Authors Su Y, Hu J, Huang Z, Huang Y, Peng B, Xie N, Liu H
Received 10 November 2016
Accepted for publication 16 January 2017
Published 6 March 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 659—668
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S127328
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Rasika Samarasinghe
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios Panos
Abstract: Malignant melanoma (MM) is the most dangerous type of skin cancer with
annually increasing incidence and death rates. However, chemotherapy for MM is
restricted by low topical drug concentration and multidrug resistance. In order
to surmount the limitation and to enhance the therapeutic effect on MM, a new
nanoformulation of paclitaxel (PTX)-loaded cholic acid (CA)-functionalized
star-shaped poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA)-d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene
glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) nanoparticles (NPs) (shortly PTX-loaded
CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs) was fabricated by a modified method of nanoprecipitation. The
particle size, zeta potential, morphology, drug release profile, drug
encapsulation efficiency, and loading content of PTX-loaded NPs were detected.
As shown by confocal laser scanning, NPs loaded with coumarin-6 were
internalized by human melanoma cell line A875. The cellular uptake efficiency
of CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs was higher than those of PLGA NPs and PLGA-TPGS NPs. The
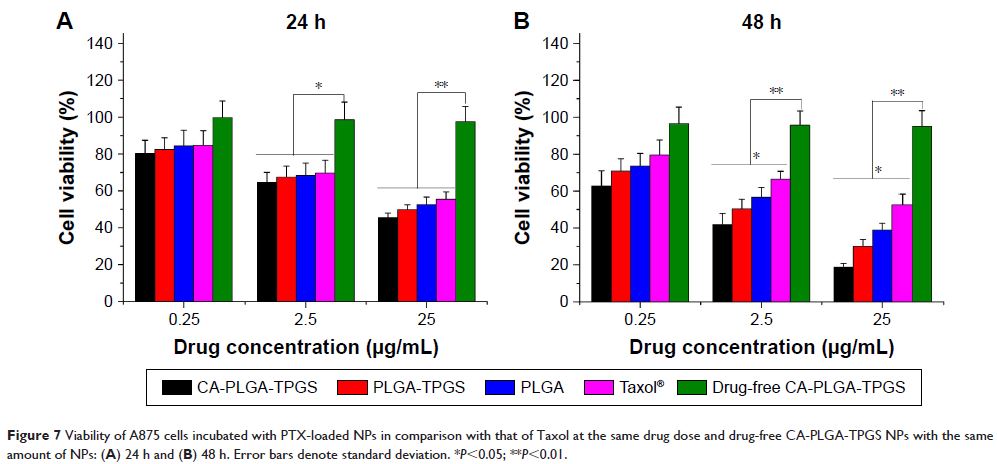
antitumor effects of PTX-loaded NPs were evaluated by the MTT assay in vitro
and by a xenograft tumor model in vivo, demonstrating that star-shaped
PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were significantly superior to commercial PTX
formulation Taxol®. Such drug delivery
nanocarriers are potentially applicable to the improvement of clinical MM
therapy.
Keywords: malignant melanoma, paclitaxel,
nanoparticles, enhanced therapeutic effects, drug delivery