109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

HMGB1 与子宫内膜癌的发生呈负相关,通过抑制上皮间质转化过程阻止癌细胞侵袭和转移
Authors Luan XR, Ma CJ, Wang P, Lou FL
Received 23 September 2016
Accepted for publication 18 November 2016
Published 3 March 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1389—1402
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S123085
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashok Kumar Pandurangan
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Abstract: High-mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1), a nuclear protein that plays
a significant role in DNA architecture and transcription, was correlated with the
progression of some types of cancer. However, the role of HMGB1 in endometrial
cancer cell invasion and metastasis remains unexplored. HMGB1 expression was
initially assessed by immunohistochemistry and reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) in normal
endometrial tissue and endometrial carcinoma tissue. High expressions of HMGB1
protein were detected in normal endometrial tissues; however, in endometrial
cancer tissues, the expressions of HMGB1 were found to be very weak. Furthermore,
HMGB1 expressions were negatively correlated with advanced stage and lymph node
metastasis in endometrial cancer. Then by RT-qPCR, Western blot and
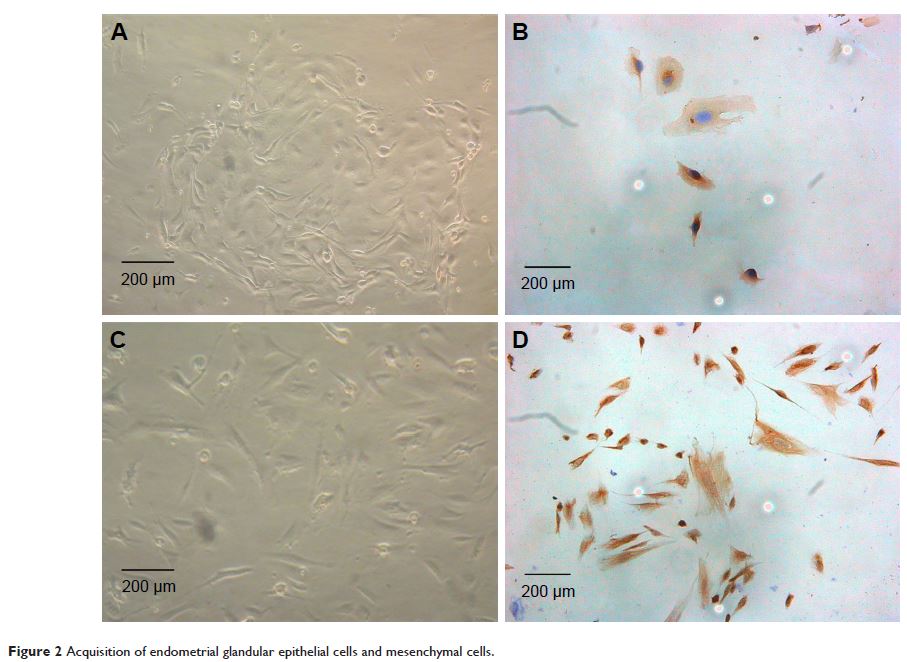
immunocytochemistry, HMGB1 was also detected in primary cultured endometrial
cells and four kinds of endometrial cancer cell lines (Ishikawa, HEC-1A, HEC-1B
and KLE). We found that the expression of HMGB1 was much higher in normal
endometrial cells than in endometrial cancer cells, and reduced expression
levels of HMGB1 were observed especially in the highly metastatic cell lines.
Using lentivirus transfection, HMGB1 small hairpin RNA was constructed, and
this infected the lowly invasive endometrial cancer cell lines, Ishikawa and
HEC-1B. HMGB1 knockdown significantly enhanced the proliferation, invasion and
metastasis of endometrial cancer cells and induced the process of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. These results can contribute to the
development of a new potential therapeutic target for endometrial cancer.
Keywords: HMGB1, endometrial cancer, invasion,
metastasis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition