109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用微阵列基因表达图谱和基因相互作用网络确定与人类多发性骨髓瘤卡非佐米 (Carfilzomib) 耐药相关的分子机制
Authors Zheng Z, Liu T, Zheng J, Hu J
Received 20 December 2016
Accepted for publication 14 January 2017
Published 1 March 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1327—1334
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S130742
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Abstract: Carfilzomib is a Food and Drug Administration-approved
selective proteasome inhibitor for patients with multiple myeloma (MM).
However, recent studies indicate that MM cells still develop resistance to
carfilzomib, and the molecular mechanisms associated with carfilzomib
resistance have not been studied in detail. In this study, to better understand
its potential resistant effect and its underlying mechanisms in MM, microarray
gene expression profile associated with carfilzomib-resistant KMS-11 and its
parental cell line was downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus database. Raw
fluorescent signals were normalized and differently expressed genes were
identified using Significance Analysis of Microarrays method. Genetic
interaction network was expanded using String, a biomolecular interaction
network JAVA platform. Meanwhile, molecular function, biological process and
signaling pathway enrichment analysis were performed based on Gene Ontology and
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Totally, 27 upregulated and 36
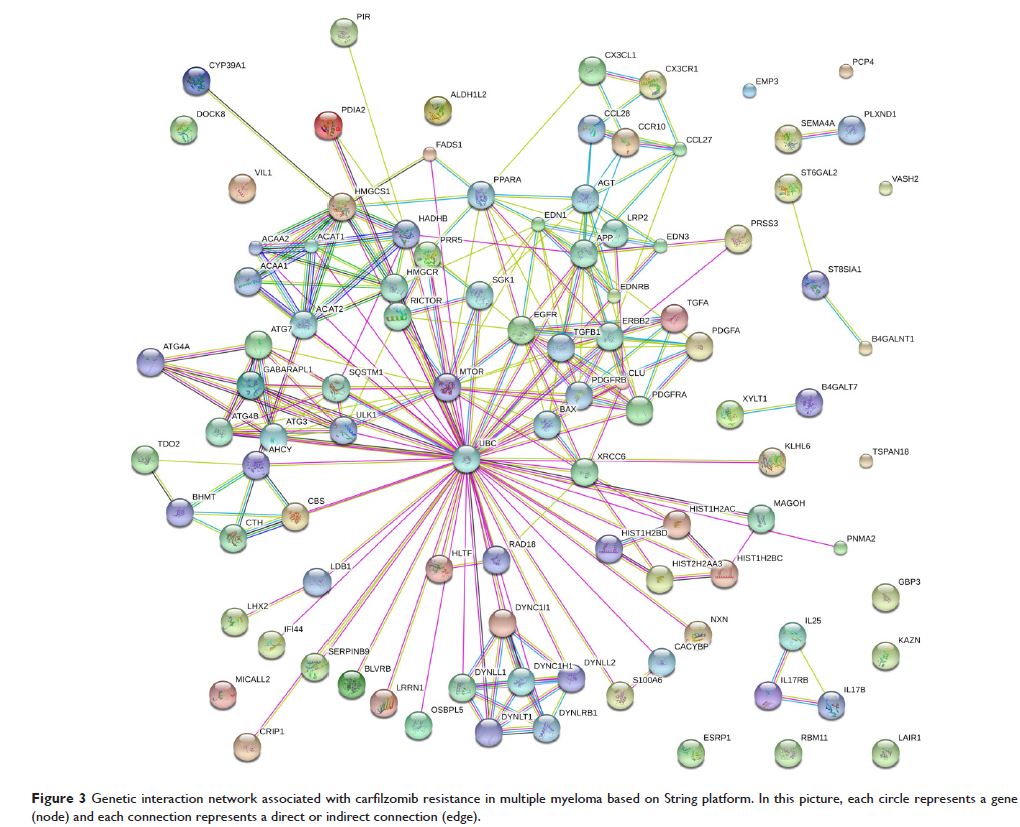
downregulated genes were identified and a genetic interaction network
associated with the resistant effect was expanded basing on String, which
consisted of 100 nodes and 249 edges. In addition, signaling pathway enrichment
analysis indicated that cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, autophagy, ErbB
signaling pathway, microRNAs in cancer and fatty acid metabolism pathways were
aberrant in carfilzomib-resistant KMS-11 cells. Thus, in this study, we
demonstrated that carfilzomib potentially conferred drug resistance to KMS-11
cells by cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, autophagy, ErbB signaling
pathway, microRNAs in cancer and fatty acid metabolism pathways, which may
provide some potential molecular therapeutic targets for drug combination
therapy against carfilzomib resistance.
Keywords: multiple myeloma, carfilzomib, drug
resistance, microarray, interaction network, compensate pathways