109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

术前 CEA 和 CA19-9 的组合改进了对可切除胰腺腺癌患者的预测结果: 来自大型后续队列研究的结果
Authors Zhou G, Liu X, Wang X, Jin D, Chen Y, Li G, Li C, Fu D, Xu W, Wang X
Received 30 June 2016
Accepted for publication 18 November 2016
Published 24 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1199—1206
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S116136
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Abstract: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most lethal
malignancies with a 5-year survival rate of <7%. Carbohydrate antigen 19-9
(CA19-9) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) are often used to predict the
outcome of the malignancy independently. However, the joint prognostic effect
of the two tumor biomarkers has not been well determined. The study assessed
the joint role of preoperative CA19-9 and CEA in the prognostic prediction of
resectable PDAC in a large cohort of patients. The study enrolled 460 eligible
patients who were ready to undergo surgery for PDAC. Restricted cubic spline
and direct-adjusted survival curve revealed the nonlinear association between
the biomarker levels and prognosis of patients. Combination of preoperative
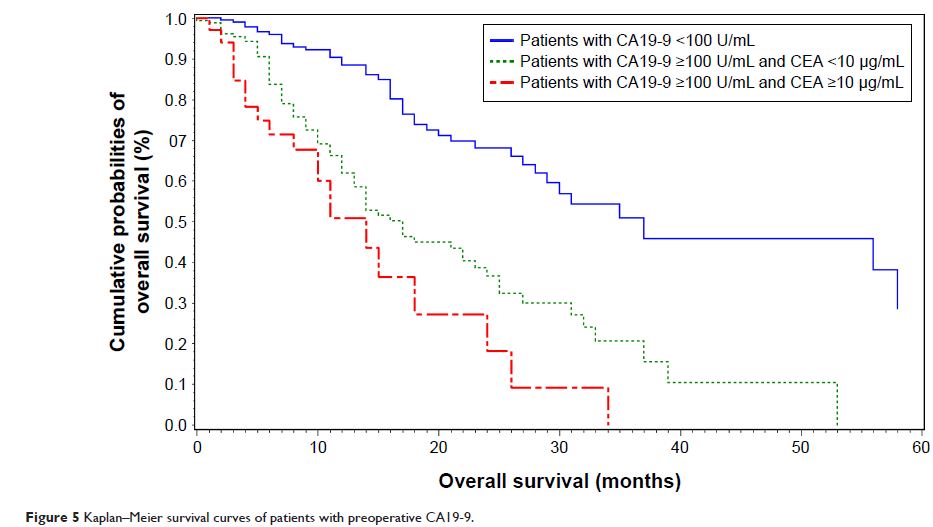
CA19-9 and CEA effectively improved the prognostic prediction. About 100 U/mL
of CA19-9 and 10 µg/mL of CEA were revealed as potential assistant index for
prognostic prediction in patients with resectable PDAC and may be used as one
of the criteria to assess the resectability of PDAC.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer, prognosis, tumor
biomarkers, CA19-9, CEA