109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

封装紫杉醇 (Paclitaxel) 和厚朴酚 (honokiol) 的生物可降解聚合物胶束:乳腺癌体外和体内的治疗策略
Authors Wang N, Wang Z, Nie S, Song L, He T, Yang S, Yang X, Yi C, Wu Q, Gong C
Received 17 October 2016
Accepted for publication 16 January 2017
Published 23 February 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1499—1514
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S124843
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: The combination of chemotherapy drugs attracts more attention in
clinical cancer trials. However, the poor water solubility of chemotherapeutic
drugs restricts their anticancer application. In order to improve antitumor
efficiency and reduce side effects of free drugs, we prepared paclitaxel (PTX)
and honokiol (HK) combination methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(caprolactone)
micelles (P–H/M) by solid dispersion method against breast cancer.
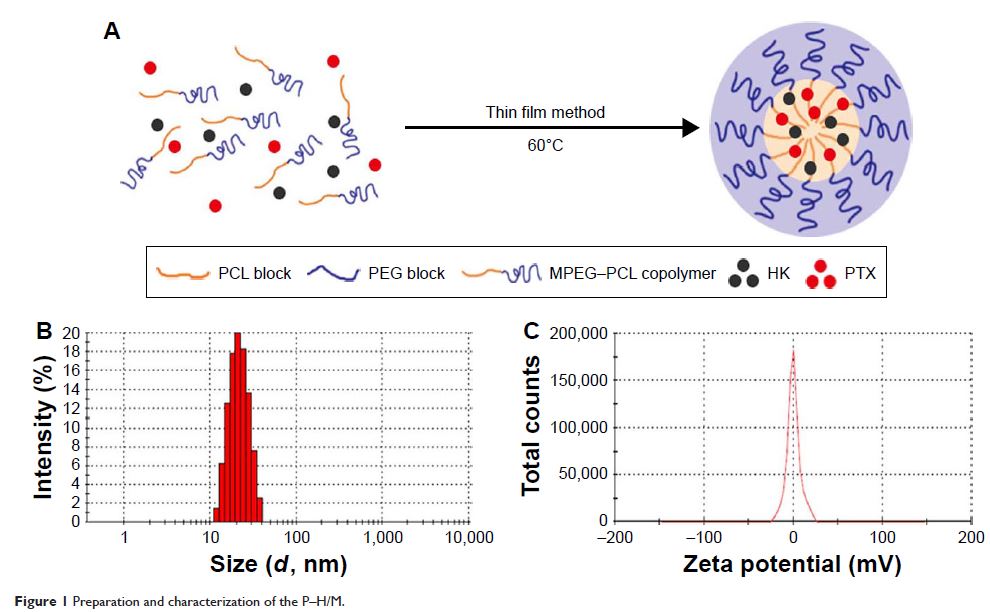
The particle size of P–H/M was 28.7±2.5 nm, and transmission electron
microscope image confirmed that P–H/M were spherical in shape with small
particle size. After being encapsulated in micelles, the release of PTX or HK
showed a sustained behavior in vitro. In addition, both the cytotoxicity and the
cellular uptake of P–H/M were increased in 4T1 cells, and P–H/M induced more
apoptosis than PTX-loaded micelles or HK-loaded micelles, as analyzed by flow
cytometry assay and Western blot. Furthermore, the antitumor effect of P–H/M
was significantly improved compared with PTX-loaded micelles or HK-loaded
micelles in vivo. P–H/M were more effective in inhibiting tumor proliferation,
inducing tumor apoptosis, and decreasing the density of microvasculature.
Moreover, bioimaging analysis showed that drug-loaded polymeric micelles could
accumulate more in tumor tissues compared with the free drug. Our results
suggested that P–H/M may have potential applications in breast cancer therapy.
Keywords: paclitaxel,
honokiol, micelles, codelivery, breast cancer