109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

慢性淋巴细胞患者 CD19+ B 细胞中的异常组蛋白修饰
Authors Zhou K, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Xiong Y, Wu S, Yang J, Zhou H, Liu X, Wei X, Song Y
Received 2 September 2016
Accepted for publication 9 December 2016
Published 23 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1173—1179
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S121301
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Abstract: The aim of this study was to detect the alterations in histone
methylation and acetylation in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
(CLL). Global histone H3/H4 acetylation and H3K4/H3K9 methylation were detected
by the EpiQuik™ global histone H3/H4 acetylation and H3K4/H3K9 methylation
assay kits. The mRNA expression of selected chromatin modifier genes was
measured by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Our results found
that the global histone H3/H4 hypoacetylation in the CD19+ B
cells of patients with CLL (P =0.028 and P =0.03,
respectively) and the global histone H3K9 methylation in patients with CLL were
significantly increased compared with controls (P =0.02),
while there was no significant difference in the global histone H3K4
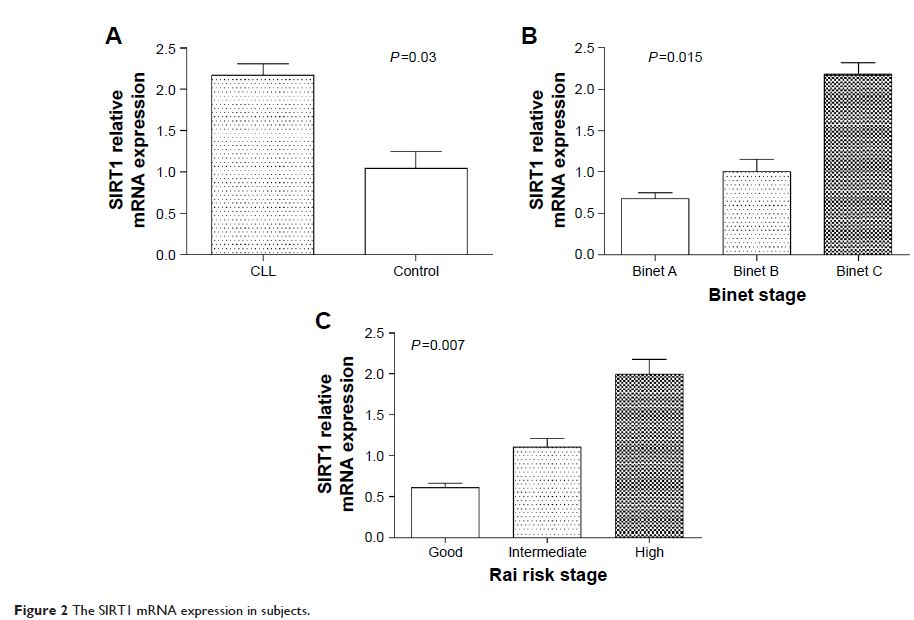
methylation between the two groups. The level of SIRT1 and EZH2 mRNA expression
was upregulated in patients with CLL (P =0.03 and P =0.02, respectively), which
increased significantly with progression from Binet stage A to stage C (P =0.015 and P =0.01,
respectively) and Rai good to high risk stage (P =0.007
and P =0.008,
respectively). The level of HDAC1 and HDAC7 mRNA expression was significantly
increased (P =0.02 and P =0.008, respectively)
and HDAC2 and P300 mRNA expression was reduced in patients with CLL (P =0.002 and P =0.001,
respectively). In conclusion, it is observed that the aberrant histone
modification plays an important role in the pathogenesis of CLL.
Keywords: histone
methylation, histone acetylation, SIRT1, EZH2, CLL