109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

含水溶性烟酰胺 (Nicotinamide) 的纳米颗粒对他克莫司 (tacrolimus) 的影响:透过银屑病皮肤的渗透性,以及抗银屑病和抗增殖活性
Authors Wan T, Pan W, Long Y, Yu K, Liu S, Ruan W, Pan J, Qin M, Wu C, Xu Y
Received 31 October 2016
Accepted for publication 2 January 2017
Published 22 February 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1485—1497
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S126210
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: The hybrid system based on nanoparticles (NPs) self-assembled by the
conjugations of hyaluronic acid with cholesterol (HA–Chol NPs) combined with
nicotinamide (NIC) for tacrolimus (FK506), ie, FK506 NPs–NIC, has been
confirmed to exhibit a significant synergistic effect on FK506 permeation
through and into intact skin; thus, it may be a promising approach for FK506 to
effectively treat skin diseases. The aim of this study was to evaluate its
potential for the treatment of psoriasis. In vitro permeation through the
psoriatic skin was carried out, and the results revealed that the combination
of NPs with NIC exhibited a significant synergistic effect on FK506 deposition
within the psoriatic skin (3.40±0.67 µg/cm2) and penetration
through the psoriatic skin (30.86±9.66 µg/cm2). The antipsoriatic
activity of FK506 NPs–NIC was evaluated through the treatment for imiquimod
(IMQ)-induced psoriasis. The psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score
demonstrated that FK506 HA–Chol NPs–NIC exerted the effect on ameliorating the
skin lesions comparable to clobetasol propionate (a positive drug for
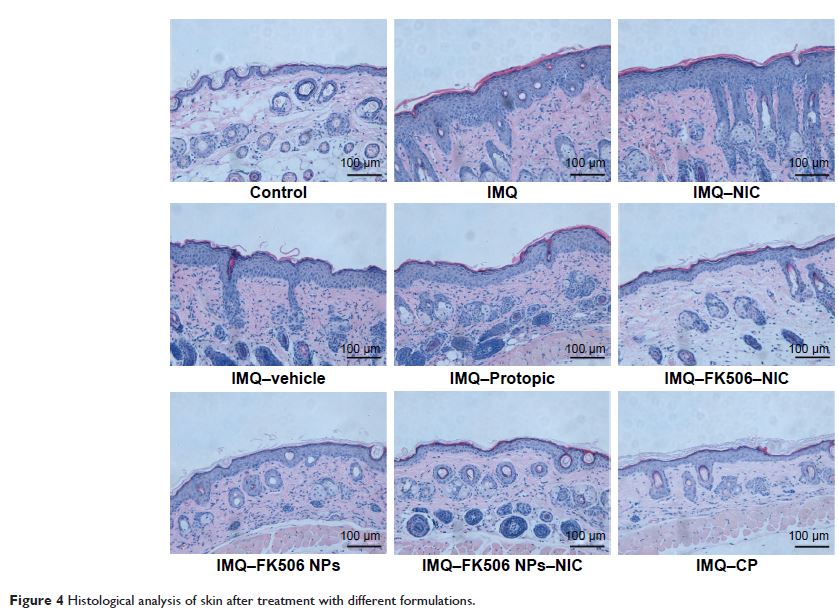
psoriasis) and superior to commercial FK506 ointment (Protopic®), and the histological study showed that it
presented a synergistic effect on antipsoriasis after FK506 incorporation into
NPs combined with NIC hydrotropic system, which might ultimately increase the
therapeutic effect and minimize the systemic side effects by reducing the
overall dose of FK506. RAW 264.7 cell uptake presented the enhancement of drugs
delivered into cells by HA–Chol NPs–NIC. The antiproliferative activity on
HaCaT cells identified that FK506 HA–Chol NPs–NIC exhibited significant
inhibiting effects on HaCaT proliferation. The results support that the
combination of HA–Chol NPs with NIC is a promising approach for FK506 for the
treatment of psoriasis.
Keywords: tacrolimus,
nanoparticles, nicotinamide, percutaneous delivery, psoriasis,
antiproliferation