109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

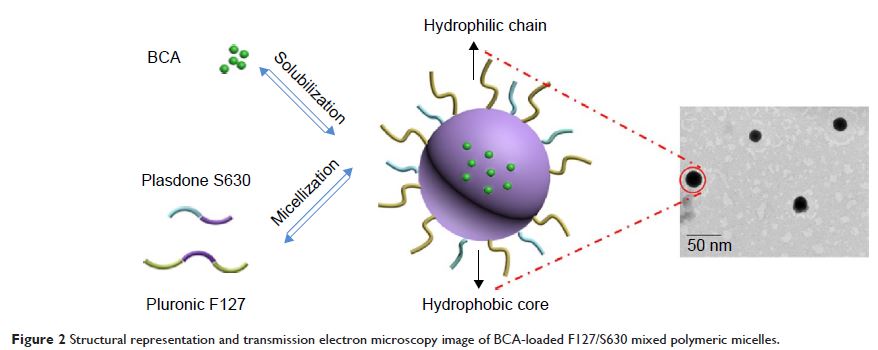
将 Pluronic F127 和 Plasdone S630 封装在混合胶束中提高鹰嘴豆素 A (Biochanin A) 的口服生物利用度
Authors Wu X, Ge W, Shao T, Wu W, Hou J, Cui L, Wang J, Zhang Z
Received 18 October 2016
Accepted for publication 11 January 2017
Published 22 February 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1475—1483
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S125041
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jiang Yang
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Biochanin A (BCA), a natural dietary isoflavone, has been reported to
show anticancer activities. However, its low biological availability and poor
aqueous solubility limit its usefulness as a chemotherapeutic agent. We
developed BCA-loaded micelles with Pluronic F127 and Plasdone S630 (BCA-FS).
The optimized, spherical-shaped BCA-FS was obtained at a ratio of 1:1
(F127:S630). The particle size was 25.17±1.2 nm, and the zeta potential was −10.9±0.24
mV. BCA solubility in water increased to 5.0 mg/mL after encapsulation, and the
drug-loading efficiency was 5.88%±0.76%. In vitro release experiments showed a
delayed release of BCA from the mixed micelles. Furthermore, the BCA absorption
permeability across a Caco-2 cell monolayer from the apical side to the
basolateral side increased by 54% in BCA-FS. A pharmacokinetics evaluation
showed a 2.16-fold increase in the relative oral bioavailability of BCA-FS
compared with raw BCA, indicating that the mixed micelles may promote
absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. A gastrointestinal safety assay was
used to assess the reliability and safety of BCA-FS. On the basis of these
findings, we conclude that this simple nanomicelle system could be leveraged to
deliver BCA and other hydrophobic drugs.
Keywords: biochanin
A, mixed micelles, oral bioavailability, Pluronic F127, Plasdone S630