109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

微 RNA-149-3p 对 Toll 样受体-4 的抑制与吸烟相关的 COPD 有关
Authors Shen W, Liu J, Zhao G, Fan M, Song G, Zhang Y, Weng Z, Zhang Y
Received 17 November 2016
Accepted for publication 27 December 2016
Published 22 February 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 705—715
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S128031
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Charles Downs
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Background: Smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Exploring molecular
markers and understanding the pathogenic mechanisms of smoking-related COPD are
helpful for early clinical diagnosis and treatment of the disease. This study
aims to identify specific circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) from the blood of COPD
patients with a long history of smoking.
Methods: Blood samples from four different groups were
collected, and miRNA microarray was performed. Differential expression of
miRNAs was verified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. In vitro, THP-1
cells were cultured and stimulated with cigarette smoke extract (CSE) or
transfected with miR-149-3p inhibitor/mimics. Protein levels of Toll-like
receptor 4 (TLR-4) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) were detected using Western
blot and immunofluorescence. Interleukin (IL)-1β and tumor necrosis factor
(TNF)-α levels were determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results: miRNA profiling revealed that the expression of 56
miRNAs was changed between the four groups. Expression of miR-149-3p in group C
(non-smoker non-COPD) was higher than in group S (smoker non-COPD), S-COPD
(smoker with stable COPD) and AE-COPD (smoker with acute exacerbation COPD).
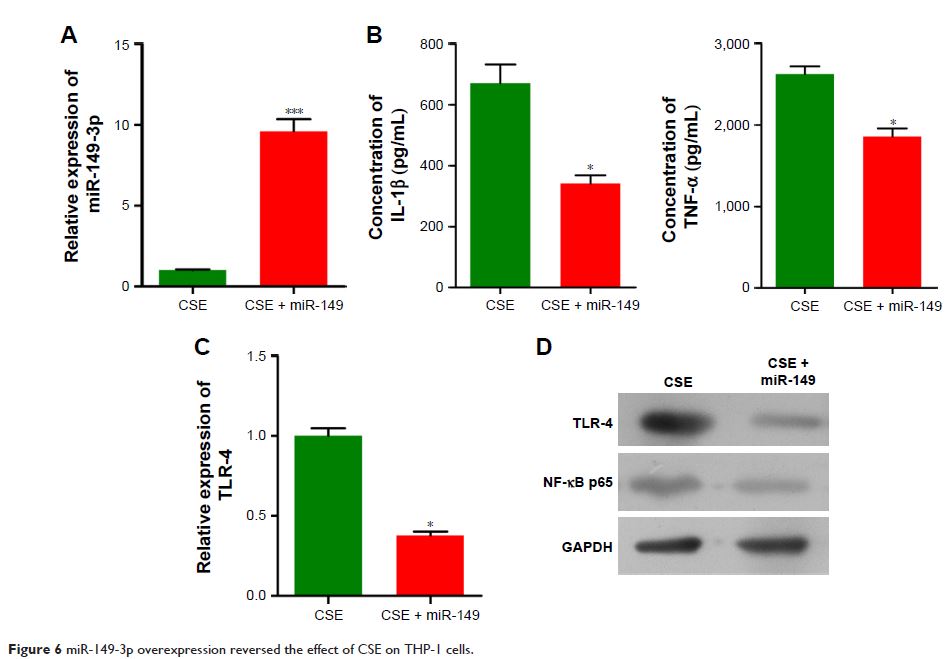
CSE stimulation down-regulated the expression of miR-149-3p and up-regulated
the TLR-4 and NF-κB levels in THP-1 cells. Transfecting miR-149-3p inhibitors
in THP-1 cells also increased the expression of its target genes. Furthermore,
overexpression of miR-149-3p inhibited the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathways and
reduced the secretion of IL-1β and TNF-α.
Conclusion: This study found that smoking can induce differential
expression of circulating miRNAs, such as down-regulation of miR-149-3p.
Reducing miR-149-3p may increase the inflammatory response in COPD patients
through the regulation of the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: smoking, COPD, microRNA-149-3p,
Toll-like receptor 4, nuclear factor κB