109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
功能性姜黄素 (Curcumin) 脂质体在体外和动物中诱导 C6 胶质母细胞瘤细胞和 C6 胶质母细胞瘤干细胞的凋亡
Authors Wang YH, Ying X, Xu HL, Yan HL, Li X, Tang H
Received 10 October 2016
Accepted for publication 20 December 2016
Published 17 February 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1369—1384
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S124276
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
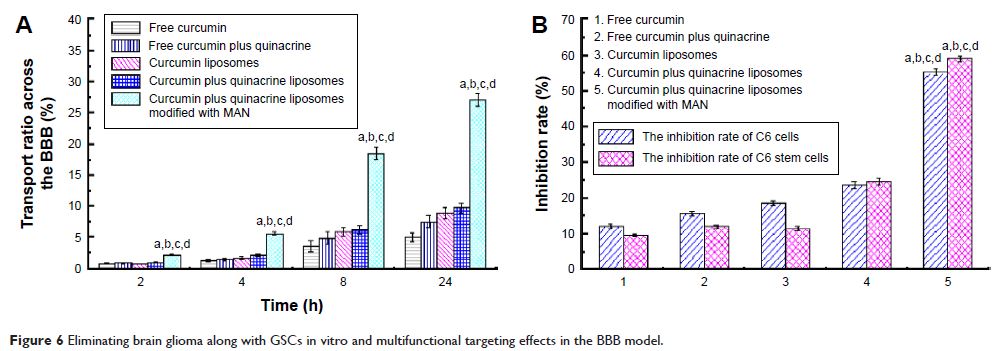
Abstract: Glioblastoma is a
kind of malignant gliomas that is almost impossible to cure due to the poor
drug transportation across the blood–brain barrier and the existence of glioma
stem cells. We prepared a new kind of targeted liposomes in order to improve
the drug delivery system onto the glioma cells and induce the apoptosis of
glioma stem cells afterward. In this experiment, curcumin was chosen to kill
gliomas, while quinacrine was used to induce apoptosis of the glioma stem
cells. Also, p -aminophenyl-α-d-mannopyranoside
could facilitate the transport of liposomes across the blood–brain barrier and
finally target the brain glioma cells. The cell experiments in vitro indicated
that the targeted liposomes could significantly improve the antitumor effects
of the drugs, while enhancing the uptake effects, apoptosis effects, and
endocytic effects of C6 glioma cells and C6 glioma stem cells. Given the animal
experiments in vivo, we discovered that the targeted liposomes could obviously
increase the survival period of brain glioma-bearing mice and inhibit the
growth of gliomas. In summary, curcumin and quinacrine liposomes modified with p -aminophenyl-α-d-mannopyranoside
is a potential preparation to treat brain glioma cells and brain glioma stem
cells.
Keywords: C6 glioblastoma stem cells, apoptosis, blood–brain barrier, curcumin liposomes, brain glioma-bearing rats
Keywords: C6 glioblastoma stem cells, apoptosis, blood–brain barrier, curcumin liposomes, brain glioma-bearing rats