109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过理论研究了解 AZD4547 和 E3810 对 FGFR1 把关突变的抗性机制
Authors Liang D, Chen Q, Guo Y, Zhang T, Guo W
Received 11 December 2016
Accepted for publication 6 January 2017
Published 17 February 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 451—461
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S129991
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Abstract: Inhibitors targeting the amplification of the fibroblast
growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) have found success in the treatment of
FGFR1-positive squamous cell lung and breast cancers. A secondary mutation of
gatekeeper residue (V561M) in the binding site has been linked to the acquired
resistance. Recently, two well-known small molecule inhibitors of FGFR1, AZD4547
and E3810, reported that the V561M mutation confers significant resistance to
E3810, while retaining affinity for AZD4547. FGFR1 is widely investigated as
potential therapeutic target, while there are few computational studies made to
understand the resistance mechanisms about FGFR1 V561M gatekeeper mutation. In
this study, molecular docking, classical molecular dynamics simulations,
molecular mechanics/generalized born surface area (MM/GBSA) free energy
calculations, and umbrella sampling (US) simulations were carried out to make
clear the principle of the binding preference of AZD4547 and E3810 toward FGFR1
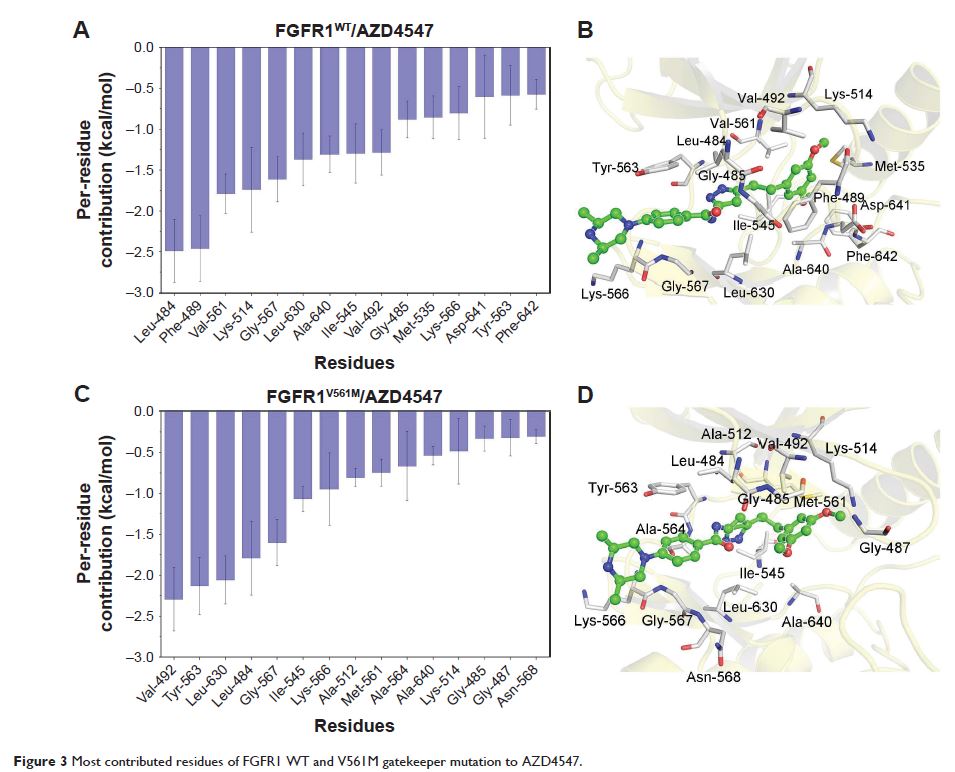
V561M gatekeeper mutation. The results provided by MM/GBSA reveal that AZD4547
has similar binding affinity to both FGFR1WT and FGFR1V561M,
whereas E3810 has much higher binding affinity to FGFR1WT than
to FGFR1V561M. Comparison of individual energy terms
indicates that the major variation of E3810 between FGFR1WT and
FGFR1V561M are
van der Waals interactions. In addition, US simulations prove that the
potential of mean force (PMF) profile of AZD4547 toward FGFR1WT and
FGFR1V561M has
similar PMF depth. However, the PMF profile of E3810 toward FGFR1WT and
FGFR1V561M has
much higher PMF depth, suggesting that E3810 is more easily dissociated from
FGFR1V561M than
from FGFR1WT. The results not only show the drug-resistance
determinants of FGFR1 gatekeeper mutation but also provide valuable
implications and provide vital clues for the development of new inhibitors to
combat drug resistance.
Keywords: FGFR1, gatekeeper
mutation, V561M, theoretical study, resistance mechanisms