109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过递送 3-十八烷基氨基甲酰丙烯酸 - 顺铂 (Cisplatin) 脂质体来逆转人肺癌细胞中的多药耐药性
Authors Song J, Ren W, Xu T, Zhang Y, Guo H, Zhu S, Yang L
Received 17 October 2016
Accepted for publication 16 November 2016
Published 17 February 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 441—449
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S124912
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Abstract: Liposome-based drug delivery system would be an innovative and promising
candidate to circumvent multidrug resistance (MDR) of cisplatin (CDDP).
However, the reversal efficacy of liposomal CDDP was severely impaired by weak
cellular uptake and insufficient intracellular drug release. In this study,
3-octadecylcarbamoylacrylic acid–CDDP nanocomplex (OMI–CDDP–N)-based liposomes
(OCP-L) with high cellular uptake and sufficient intracellular drug release
were designed to circumvent MDR of lung cancer. OMI–CDDP–N was synthesized
through a pH-sensitive monocarboxylato and an O→Pt coordinate bond, which is more
efficient than CDDP. Also, OCP-L incorporated with OMI–CDDP–N could induce
effective cellular uptake, enhanced nuclear distribution, and optimal cellular
uptake kinetics. In particular, OCP-L presented superior effects on enhancing
cell apoptosis and in vitro cytotoxicity in CDDP-resistant human lung cancer
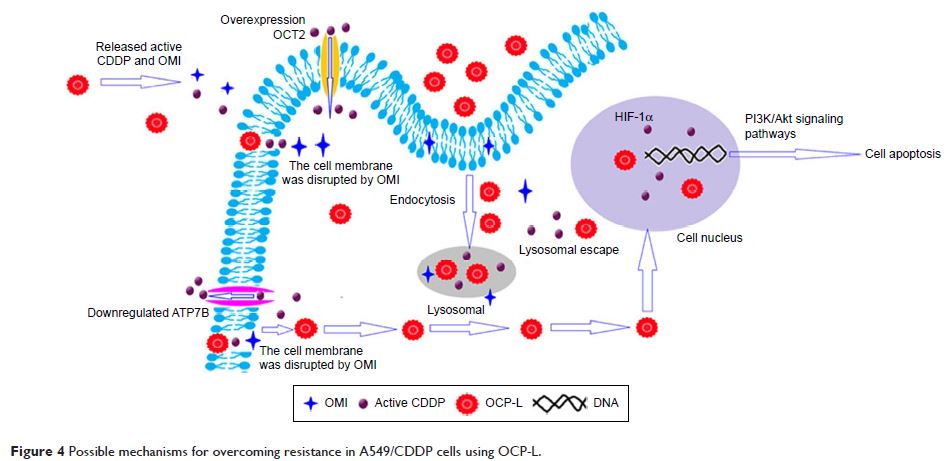
(A549/CDDP) cells. The mechanisms of MDR reversal in A549/CDDP cells by OCP-L
could attribute to organic cation transporter 2 restoration, ATPase
copper-transporting beta polypeptide suppression, hypoxia-inducible factor 1
α-subunit depletion, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway inhibition.
These results demonstrated that OCP-L may provide an effective delivery of CDDP
to resistant cells to circumvent MDR and enhance the therapeutic index of the
chemotherapy.
Keywords: 3-octadecylcarbamoylacrylic
acid-cisplatin nanocomplexes, liposomes, cellular uptake, multidrug resistance,
therapeutic index