109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

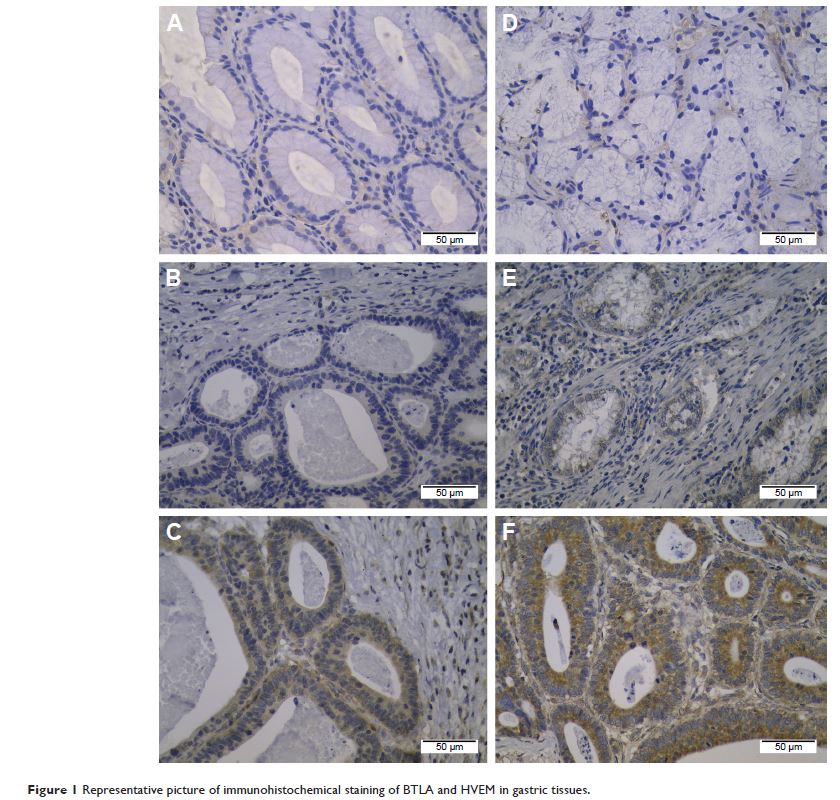
胃癌中 BTLA 和 HVEM 的增加与病情进展和不良预后相关
Authors Lan X, Li S, Gao H, Nanding A, Quan L, Yang C, Ding S, Xue Y
Received 29 November 2016
Accepted for publication 5 January 2017
Published 16 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 919—926
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S128825
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ru Chen
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Purpose: Deregulation of immune checkpoint molecules by tumor cells is related to
immune escape. This study was conducted to investigate the relationship between
the appearance of B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) and its ligand
herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM) with the prognosis in gastric cancer
patients.
Patients and methods: A total of 136 patients with curative gastrectomy were
included. The expression of BTLA and HVEM was detected by immunohistochemistry,
and its correlation with the clinical significance of gastric cancer was
further analyzed.
Results: The positivity of BTLA and HVEM was detected in 74.3%
(101/136) and 89.0% (121/136) of the gastric cancer specimens, respectively. A
high expression of BTLA and HVEM was detected, respectively, in 28.7% (39/136)
and 44.9% (61/136) of the specimens. Characteristics analysis showed that the
high expression of BTLA was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis
(P =0.030). Similarly, the high
expression of HVEM was also significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis
(P =0.007) and depth of invasion (P =0.011). In addition, there was a
positive correlation between the expression of BTLA and HVEM in gastric cancer
specimens (r =0.245, P =0.004).
Univariate analysis revealed that the high expression of BTLA and HVEM was
associated with overall survival of patients along with tumor size, Borrmann
type, depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis, and histological grade (P <0.05). Multivariate analysis
established that the high expression of HVEM (P =0.010),
depth of invasion (P =0.001), lymph node
metastasis (P <0.001), and histological
grade (P =0.027) were independent
prognostic factors associated with overall survival in patients with gastric
cancer.
Conclusion: The increased BTLA and HVEM levels correlate with the
development and poor prognosis of gastric cancer. HVEM is an important
prognostic indicator, and BTLA/HVEM pathway is considered to be a promising
candidate for immunotherapy of gastric cancer.
Keywords: gastric
cancer, B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator, herpesvirus entry mediator, prognostic