109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Polydatin 通过 mTOR/p70s6k 通路调节多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖、凋亡和自噬
Authors Yang B, Zhao S
Received 28 September 2016
Accepted for publication 29 November 2016
Published 16 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 935—944
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S123398
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashok Kumar Pandurangan
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
Background: Polydatin (PD) plays an important role in suppressing
platelet aggregation, reducing blood lipid, restoring microcirculation and protecting
from myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and shock. In addition, PD
possesses anticancer activity. However, the effect and the mechanism of PD in
regulating multiple myeloma (MM) cell survival and death are still unknown.
Methods: Cell proliferation and apoptosis of RPMI 8226 cells,
respectively, were analyzed by cell counting kit8 (CCK-8) assay and flow
cytometry. The levels of caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, caspase-9, cleaved
caspase-9, Bcl-2 and Bax were analyzed by Western blot. Autophagy induced by PD
was investigated by detecting the levels of Beclin 1, Atg5, LC3I, LC3II, HSP70
and HSP27. The autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA), mTOR/p70s6k
inhibitor rapamycin, and mTOR activator MHY1485 were used to analyze the
mechanism of cell proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy influenced by PD. The
phosphorylations of mTOR and p70s6k were detected by Western blot.
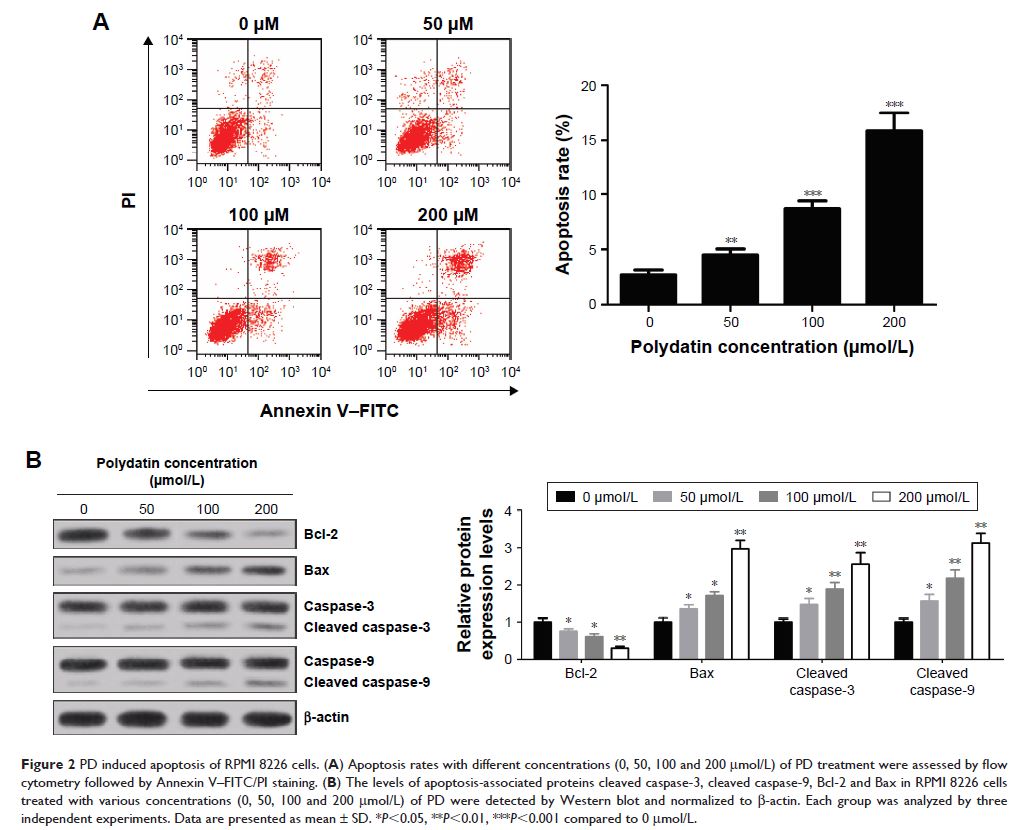
Results: A gradual decrease in cell proliferation of RPMI 8226
cells was observed with an increase in PD concentrations (P <0.05). PD also induced cell
apoptosis and autophagy in a concentration-dependent manner. Both 3-MA and
MHY1485 reversed the inhibitory effect of PD on cell proliferation and
attenuated the positive effect of PD on cell apoptosis and autophagy. The
phosphorylation of mTOR and p70s6k was significantly suppressed by PD (P <0.05). Furthermore,
inhibition of the mTOR/p70s6k signaling pathway by rapamycin significantly
induced autophagy and apoptosis and inhibited cell viability (P <0.05).
Conclusion: PD effectively suppressed cell proliferation and
induced apoptosis and autophagy of MM cells via the mTOR/p70s6k signaling
pathway in a concentration-dependent manner in vitro, indicating that PD could
be a potential anticancer drug for MM therapy.
Keywords: polydatin, proliferation, apoptosis,
autophagy, multiple myeloma, mTOR/p70s6k