109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

RACO-1 表达增加对乙型肝炎相关肝细胞癌患者的预后价值
Authors Chen JY, Liu LP, Xu JF
Received 21 October 2016
Accepted for publication 9 January 2017
Published 15 February 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 191—200
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S125331
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Hoa Le
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
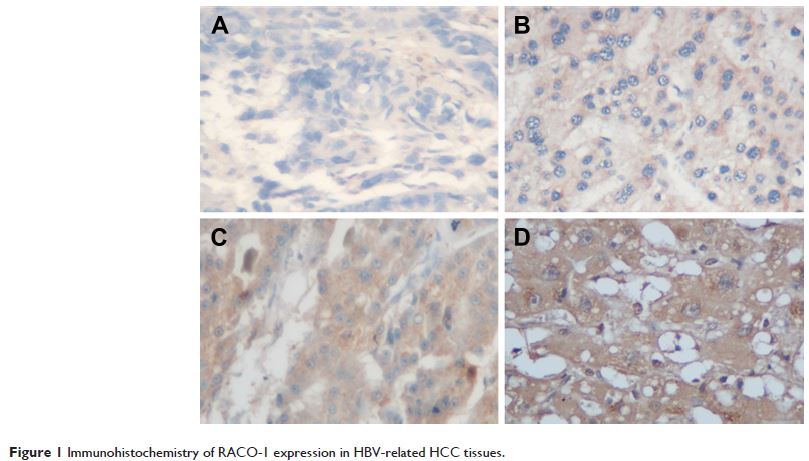
Abstract: RING domain AP-1 coactivator-1 (RACO-1) is a coactivator that links
c-Jun to growth factor signaling and is essential for AP-1 function. This study
aimed to investigate the expression and clinical significance of RACO-1 protein
in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in China. A
total of 136 tissue samples of HBV-related HCC were detected by
immunohistochemistry (including 76 patients in training cohort and 60 patients
in validation cohort). Correlation between RACO-1 expression and
clinicopathologic features of HBV-related HCC was analyzed in both the cohorts.
RACO-1 expression was significantly higher in HBV-related HCC tissues than in
adjacent non-tumor liver tissues. All the patients were divided into two
groups: the low expression group and the high expression group. RACO-1
expression was significantly related to vascular invasion (P =0.021), tumor numbers (P =0.046), International Union for
Cancer Control/American Joint Committee on Cancer stage (P =0.006), cirrhosis (P =0.046), capsular (P =0.039), and Barcelona Clinic
Liver Cancer stage (P =0.041) in
training cohort. The validation cohort showed the same results. The high RACO-1
expression was the independent prognostic factor for HBV-related HCC patients
in both training cohort and validation cohort. Our data implicate RACO-1 as a
novel prognostic marker and a potential therapeutic target for HBV-related HCC.
Keywords: RACO-1,
hepatitis B, hepatocellular carcinoma, prognosis, BCLC stage, vascular
invasion, cirrhosis, UICC/AJCC stage