109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

精神分裂症患者和他们的未患病亲属之间异常的局部连通性:对静息态功能性磁共振成像研究的一个综合分析
Authors Xiao B, Wang S, Liu J, Meng T, He Y, Luo X
Received 4 November 2016
Accepted for publication 10 January 2017
Published 14 February 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 467—475
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S126678
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Objective: The localized dysfunction of specialized brain regions in schizophrenia patients
and their unaffected relatives has been identified in a large-scale brain
network; however, evidence is inconsistent. We aimed to identify abnormalities
in the localized connectivity in schizophrenia patients and their relatives by
conducting a meta-analysis of regional homogeneity (ReHo) studies.
Methods: Fourteen studies on resting-state functional magnetic
resonance imaging, with 316 schizophrenia patients, 342 healthy controls, and
66 unaffected relatives, were included in the meta-analysis. This analysis was
performed using anisotropic effect-size-based signed differential mapping
software.
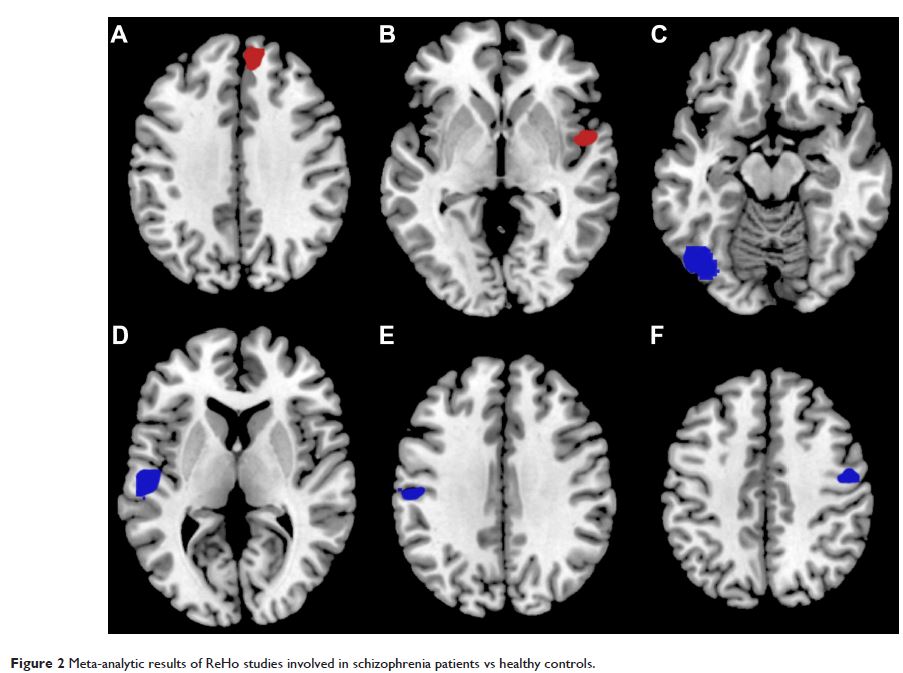
Results: Schizophrenia patients showed increased ReHo in right
superior frontal gyrus and right superior temporal gyrus, as well as decreased
ReHo in left fusiform gyrus, left superior temporal gyrus, left postcentral
gyrus, and right precentral gyrus. Unaffected relatives showed decreased ReHo
in right insula and right superior temporal gyrus. These results remained
widely unchanged in both sensitivity and subgroup analyses.
Conclusion: Schizophrenia patients and their unaffected relatives
had extensive abnormal localized connectivity in cerebrum, especially in
superior temporal gyrus, which were the potential diagnostic markers and
expounded the pathophysiological hypothesis for the disorder.
Keywords: schizophrenia, localized connectivity,
regional homogeneity, resting-state fMRI, meta-analysis, effect-size-based
signed differential mapping