109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在食管鳞状细胞癌中,通过表皮生长因子受体介导的信号传导所诱导的 PD-L1 表达
Authors Zhang W, Pang Q, Yan C, Wang Q, Yang J, Yu S, Liu X, Yuan Z, Wang P, Xiao Z
Received 4 August 2016
Accepted for publication 18 November 2016
Published 13 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 763—771
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S118982
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate the potential effect of
activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway on the
expression of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma (ESCC) cells with EGFR overexpression.
Methods: Flow cytometry and Western blot methods were used to
assess PD-L1 expression on ESCC cells when EGFR signaling pathway was activated
by epidermal growth factor (EGF) with or without EGFR-specific inhibitor
AG-1478, and then EGFR signaling array was applied to analyze the potential
signaling pathways involved.
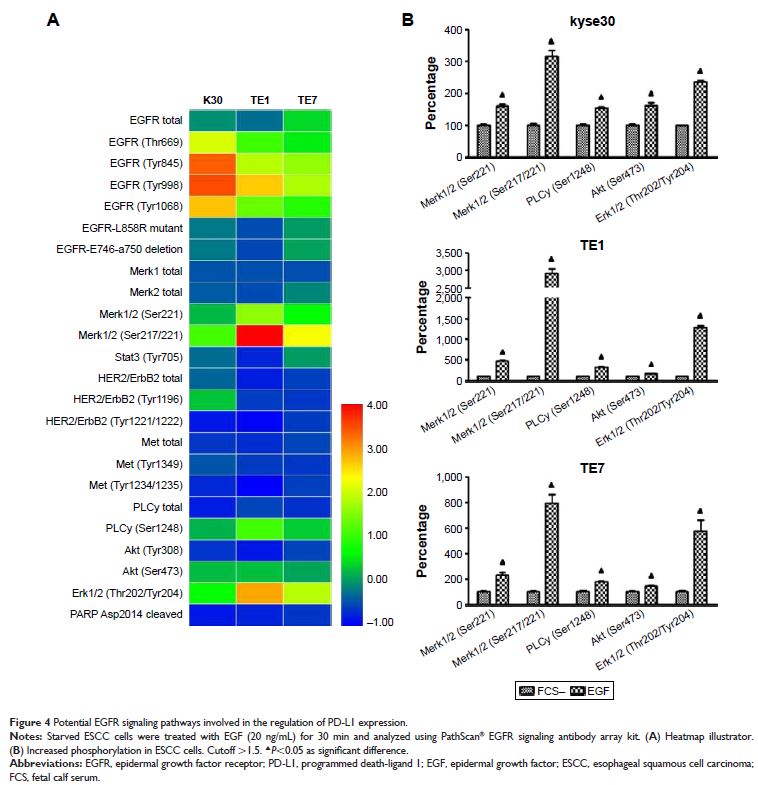
Results: This study found that PD-L1 expression increased
significantly in an EGFR-dependent manner by the activation of EGFR signaling
and decreased sharply when EGFR signaling was blocked. The upregulated
expression of PD-L1 was not associated with EGFR-STAT3 signaling pathway, but
may be affected by EGFR–PI3K–AKT, EGFR–Ras–Raf–Erk, and EGR–PLC-γ signaling
pathways.
Conclusion: The expression of PD-L1 can be regulated by EGFR
signaling activation in ESCC, which indicates an important role for
EGFR-mediated immune escape and potential molecular pathways for EGFR-targeted
therapy and immunotherapy.
Keywords: epidermal
growth factor receptor, programmed death-ligand 1, esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma, immune checkpoint