109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

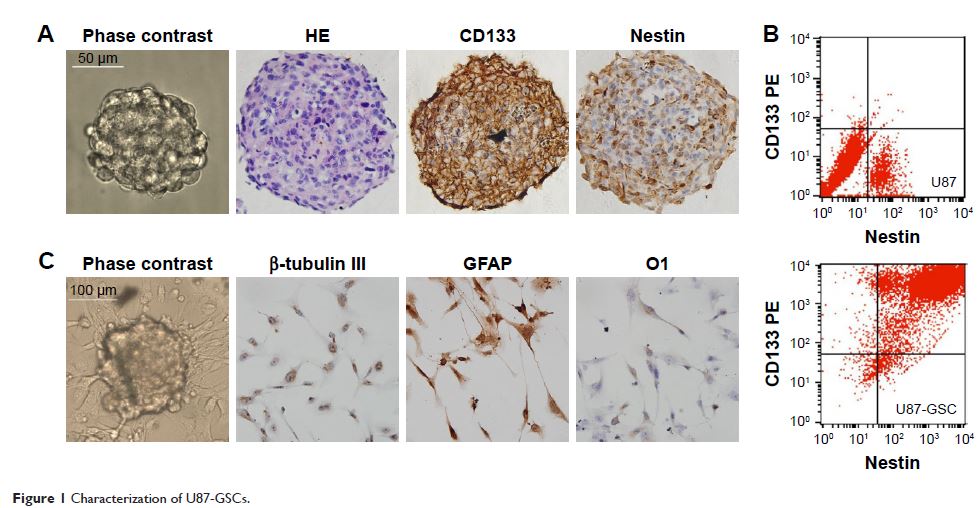
接触蛋白 2 的 RNAi 通过下调 AICD,EGFR 和 HES1 来抑制 U87 神经胶质瘤干细胞的增殖
Authors Guo Y, Zhang PD, Zhang HT, Zhang P, Xu RX
Received 23 May 2016
Accepted for publication 10 November 2016
Published 13 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 791—801
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S113390
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Abstract: Glioblastoma is the most common form of malignant brain tumors and has a
poor prognosis. Glioma stem cells (GSCs) are thought to be responsible for the
aberrant proliferation and invasion. Targeting the signaling pathways that
promote proliferation in GSCs is one of the strategies for glioma treatment. In
this study, we found increased expression of contactin 2 (CNTN2) and amyloid β
precursor protein (APP) in U87-derived GSCs (U87-GSCs). RNA interference (RNAi)
for CNTN2 downregulated the expression of APP
intracellular domain (AICD), which is the proteolytic product of APP. Treatment
with CNTN2 RNAi inhibited the proliferation of
U87-GSCs. CNTN2 RNAi decreased the expression of
epidermal growth factor receptor and HES1, which are potential targets of AICD.
In summary, inhibition of the CNTN2/APP signaling pathway may repress the
proliferation in U87-GSCs via downregulating the expression of HES1 and
epidermal growth factor receptor. CNTN2/APP/AICD signaling pathway plays an
important role in U87 glial tumorigenesis. Further studies are warranted to
elucidate the role of these signaling pathways in other sources of GSCs.
Depending on their role in proliferation in other sources of GSCs, members of
the CNTN2/APP/AICD signaling pathway may provide novel targets for the
development of therapy for glioblastomas.
Keywords: contactin 2, CNTN2, transient axonal
glycoprotein-1, TAG1, glioma stem cells