109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

二聚体肽缀合的聚赖氨酸树枝状聚合物的异构体-Fe3O4 复合物作为新型纳米级分子探针用于肝细胞癌的早期诊断和治疗
Authors Shen JM, Li XX, Fan LL, Zhou X, Han JM, Jia MK, Wu LF, Zhang XX, Chen J
Received 7 November 2016
Accepted for publication 4 January 2017
Published 10 February 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1183—1200
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S126887
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
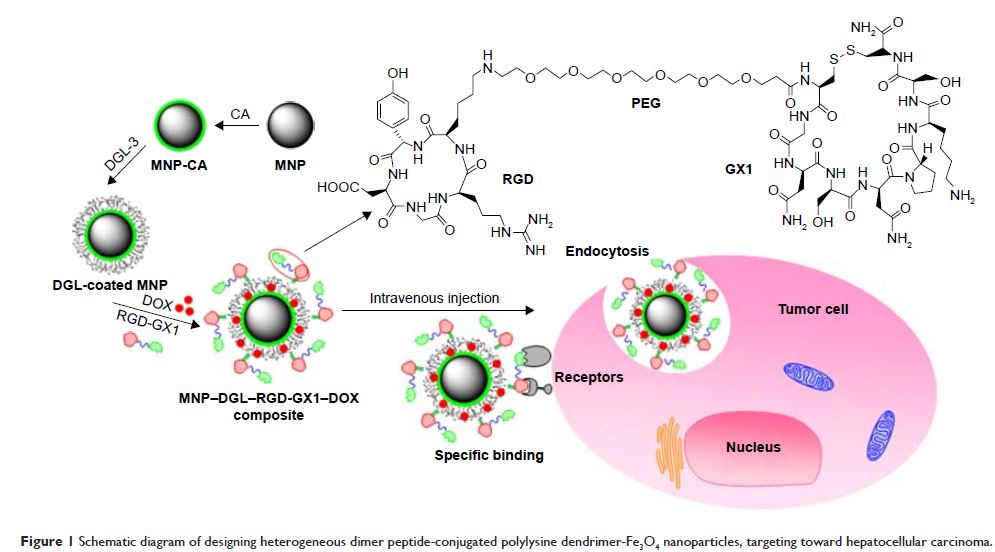
Abstract: A novel nanoscale molecular probe is formulated in order to reduce
toxicity and side effects of antitumor drug doxorubicin (DOX) in normal tissues
and to enhance the detection sensitivity during early imaging diagnosis. The
mechanism involves a specific targeting of Arg-Gly-Asp peptide (RGD)-GX1
heterogeneous dimer peptide-conjugated dendrigraft poly-l-lysine (DGL)–magnetic
nanoparticle (MNP) composite by αvβ3-integrin/vasculature endothelium receptor-mediated
synergetic effect. The physicochemical properties of the nanoprobe were
characterized by using transmission electron microscope, Fourier transform
infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and
vibrating sample magnetometer. The average diameter of the resulting
MNP–DGL–RGD-GX1–DOX nanoparticles (NPs) was ~150-160 nm by DLS under simulate
physiological medium. In the present experimental system, the loading amount of
DOX on NPs accounted for 414.4 mg/g for MNP–DGL–RGD-GX1–DOX. The results of
cytotoxicity, flow cytometry, and cellular uptake consistently indicated that
the MNP–DGL–RGD-GX1–DOX NPs were inclined to target HepG2 cells in selected
three kinds of cells. In vitro exploration of molecular mechanism revealed that
cell apoptosis was associated with the overexpression of Fas protein and the
significant activation of caspase-3. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging and
biodistribution study showed that the MNP–DGL–RGD-GX1–DOX formulation had high
affinity to the tumor tissue, leading to more aggregation of NPs in the tumor.
In vivo antitumor efficacy research verified that MNP–DGL–RGD-GX1–DOX NPs
possessed significant antitumor activity and the tumor inhibitory rate reached
78.5%. These results suggested that NPs could be promising in application to
early diagnosis and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma as a specific
nanoprobe.
Keywords: heterogeneous dimer peptide (HDP), molecular probe, magnetic
nanoparticles (MNPs), targeting, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)