109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在生物医学应用中利用超分子类肽纳米技术
Authors Chan KH, Lee WH, Zhuo S, Ni M
Received 31 October 2016
Accepted for publication 27 December 2016
Published 9 February 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1171—1182
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S126154
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Yu Mi
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: The harnessing of peptides in biomedical applications is a recent hot
topic. This arises mainly from the general biocompatibility of peptides, as
well as from the ease of tunability of peptide structure to engineer desired
properties. The ease of progression from laboratory testing to clinical trials
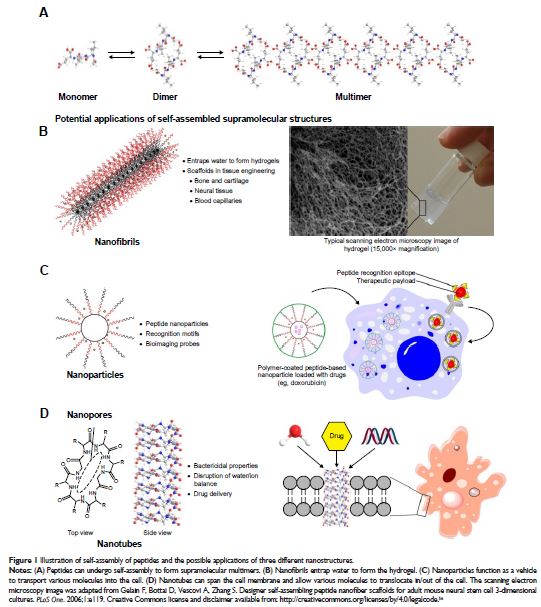
is evident from the plethora of examples available. In this review, we compare
and contrast how three distinct self-assembled peptide nanostructures possess
different functions. We have 1) nanofibrils in biomaterials that can interact
with cells, 2) nanoparticles that can traverse the bloodstream to deliver its payload
and also be bioimaged, and 3) nanotubes that can serve as cross-membrane
conduits and as a template for nanowire formation. Through this review, we aim
to illustrate how various peptides, in their various self-assembled
nanostructures, possess great promise in a wide range of biomedical
applications and what more can be expected.
Keywords: peptides, self-assembly,
nanotechnology