109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CUL4A 通过调节上皮 - 间质转化中 H3K4 的三甲基化来促进结肠直肠癌细胞的增殖和转移
Authors Sui X, Zhou H, Zhu L, Wang D, Fan S, Zhao W
Received 4 August 2016
Accepted for publication 8 December 2016
Published 9 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 735—743
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S118897
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
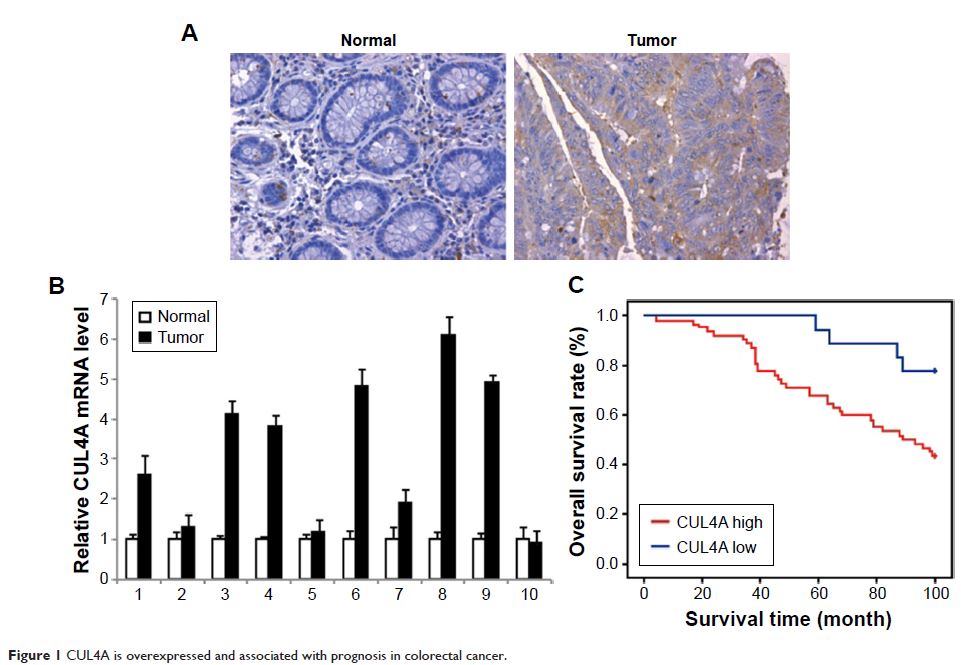
Abstract: Increasing evidence suggests that CUL4A, a ubiquitin ligase, is involved
in the promotion of cancer malignancy and correlated with worse clinical
prognosis in several kinds of human cancers. Although its effect and mechanism
on the progression of colorectal cancer (CRC) remain unknown. Our clinical data
show that CUL4A protein is overexpressed, positively associated with lymph
nodes status, differentiation degree, tumor size, and poor prognosis in 80 CRC
patients. CUL4A overexpression promotes cell proliferation and colony formation
of CRC cells. Knockdown of CUL4A inhibits cell proliferation and migration.
CUL4A can significantly promote the in vitro migration of CRC cells via
induction of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition process. And the modulation
of CUL4A expression altered the level of H3K4 trimethylation at the E-cadherin,
N-cadherin, and vimentin gene promoters, which in turn transcriptionally
regulated their expression. Moreover, knockdown of CUL4A also decreased the tumor
volume and tumor weight in vivo. Together, our results reveal that CUL4A plays
as an oncogene in CRC and may become a potential therapeutic target in the
treatment of colorectal cancer.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, CUL4A, EMT,
migration, H3K4 trimethylation