109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

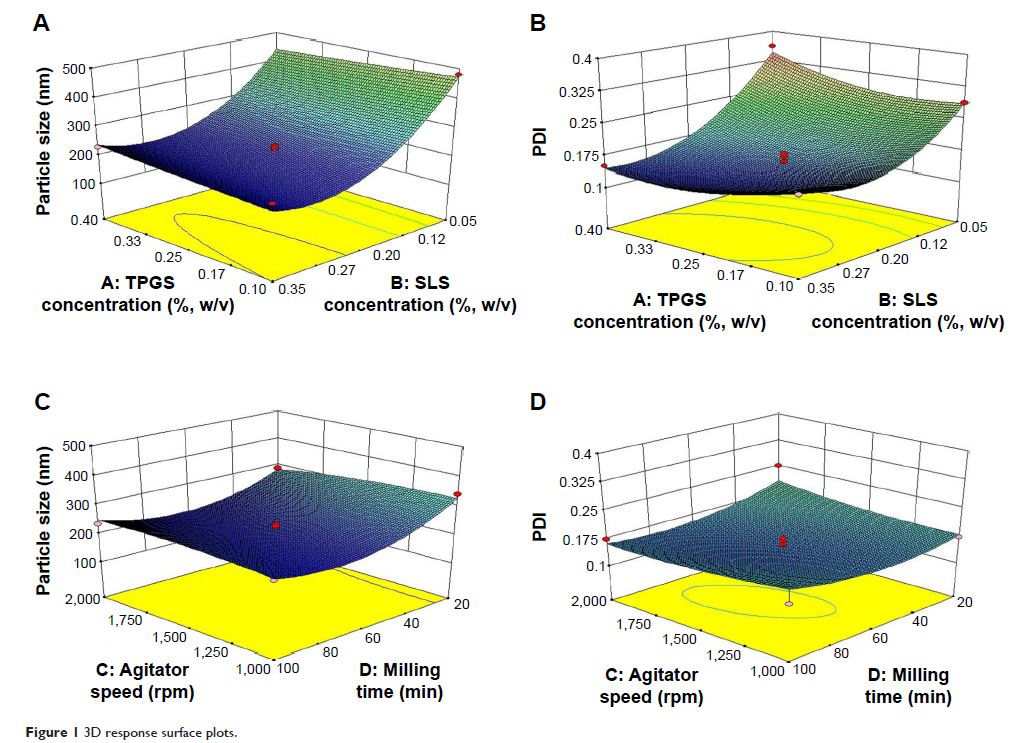
由 D-α-生育酚聚乙二醇 1000 琥珀酸 (succinate)/月桂基硫酸钠 (sodium lauryl sulfate) 稳定的无定形穿心莲内酯 (andrographolide) 纳米混悬剂的制造和体外/体内评价
Authors Qiao H, Chen L, Rui T, Wang J, Chen T, Fu T, Li J, Di L
Received 28 August 2016
Accepted for publication 30 November 2016
Published 7 February 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1033—1046
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S120887
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Andrographolide (ADG) is a diterpenoid isolated from Andrographis paniculata with a wide spectrum of biological
activities, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer and hepatoprotective
effects. However, its poor water solubility and efflux by P-glycoprotein have
resulted in lower bioavailability. In this study, ADG nanosuspensions (ADG-NS)
were prepared using a wet media milling technique followed by freeze drying.
D-α-Tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS), a surfactant that
inhibits P-glycoprotein function, and sodium lauryl sulfate were used as
surface stabilizers. A Box–Behnken design was used to optimize the
nanosuspension preparation. The products of these optimal preparation
conditions were amorphous and possessed much faster dissolution in vitro than a
coarse powder of ADG. The particle size and redispersibility index of the
freeze-dried ADG-NS were 244.6±3.0 nm and 113%±1.14% (n=3), respectively.
A short-term stability study indicated that the freeze-dried ADG-NS could
remain highly stable as nanosuspensions during the testing period. A test of
transport across a Caco-2 cell monolayer revealed that the membrane
permeability (P app) of ADG-NS was significantly higher than the permeability of the ADG
coarse powder or ADG-NS without TPGS (P <0.01).
Compared to the ADG coarse powder, a physical mixture, commercial dripping
pills and ADG-NS without TPGS, ADG-NS exhibited significantly higher plasma
exposure with significant enhancements in C max and area under the curve of plasma concentration versus time from zero
to the last sampling time (AUC0–t ) (P <0.01). An evaluation of the
anti-inflammatory effect on Carr-induced paw edema demonstrated that the ADG-NS
were more effective in reducing the rate of paw swelling, producing a greater
increase in the serum levels of nitric oxide (NO), Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and
tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (P <0.01) and an
increase in superoxide dismutase activity (P <0.05) compared
to the ADG coarse powder. This study indicated that nanosuspensions could act
as an effective delivery device for ADG to enhance its oral bioavailability and
biological efficacy.
Keywords: andrographolide, nanosuspensions, Box–Behnken design, D-α-tocopheryl
polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate, dissolution rate, oral bioavailability