109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR182 通过抑制 RASA1 和 SPRED1 激活人口腔鳞状细胞癌中的 Ras-MEK-ERK 通路
Authors Wang JH, Wang W, Li JC, Wu LJ, Song M, Meng QG
Received 8 September 2016
Accepted for publication 18 December 2016
Published 7 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 667—679
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S121864
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashok Kumar Pandurangan
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Purpose: The constitutive activation of the Ras–MEK–ERK signaling pathway in oral
cavity squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) has been found to be tightly controlled
at multiple levels under physiological conditions. RASA1 and SPRED1 are two
important negative regulators of this pathway, but the exact regulating
mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we aimed to explore the potential
regulating mechanisms involved in the Ras–MEK–ERK signaling pathway in OSCC.
Materials and
methods: MicroRNA (miRNA) expression was detected by quantitative
reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. The protein levels of RASA1,
SPRED1, and signaling proteins were detected by Western blot. Cell growth was
determined using CCK-8 reagent, colony formation was stained by crystal violet,
and cell invasion was tested using transwell chambers. Cell apoptosis and the
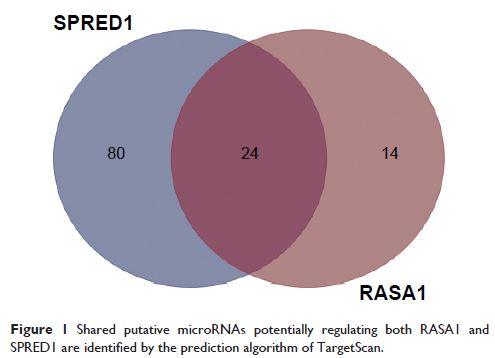
cell cycle were then analyzed by flow cytometry. The binding of miR182 with RASA1 or SPRED1 was evaluated by luciferase reporter
assays on a dual-luciferase reporter system.
Results: The expression of miR182 was found to be upregulated significantly in
malignant oral carcinoma tissues compared with the adjacent nonmalignant
tissues, and was inversely correlated with protein levels of RASA1 and SPRED1.
Overexpression of miR182 in OSCC cell lines sustained Ras–MEK–ERK
signaling-pathway activation, and promoted cell proliferation, cell-cycle
progression, colony formation, and invasion capacity, whereas miR182
downregulation alleviated these properties significantly in vitro. Furthermore,
we demonstrated that miR182 exerted its oncogenic role in OSCC by directly
targeting and suppressing RASA1 and SPRED1 .
Conclusion: Our results bring new insights into the important role of miR182 in the
activation of the Ras–MEK–ERK signaling pathway, and suggest that miR182 may be
used as a potential target for treatment of OSCC, prompting further
investigation into miRNA antisense oligonucleotides for cancer therapy.
Keywords: miR182, Ras–MEK–ERK, RASA1, SPRED1, OSCC