109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ARHGAP1 过表达抑制 C-33A 和 SiHa 细胞系的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Li JP, Liu Y, Yin YH
Received 6 May 2016
Accepted for publication 10 August 2016
Published 7 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 691—701
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S112223
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Abstract: ARHGAP1 , also known as RhoGAP , RhoGAP1 , CDC42GAP and p50rhoGAP , is officially named Ras
homology (Rho) GTPase-activating protein 1, which is one of the key members of
RhoGAPs. Growing evidences demonstrate that several RhoGAPs are suppressed or
downregulated in cancers. Thus, the aim of this study was to explore the
effects of ARHGAP1 on cervical carcinoma cells. The human
cervical carcinoma cells C-33A and SiHa were transduced with lentivirus
targeting ARHGAP1 (lenti-ARHGAP1). Cellular
proliferation, migration and invasion assays, as well as quantitative real-time
polymerase chain reaction and Western blot assays, were performed in the
control, negative control (infected with lentivirus) and ARHGAP1+-infected
groups. Results showed that overexpression of ARHGAP1 markedly
inhibited the proliferation of both C-33A and SiHa cells at 24 h,
48 h and 72 h in a time-dependent manner (n=3, P <0.01).
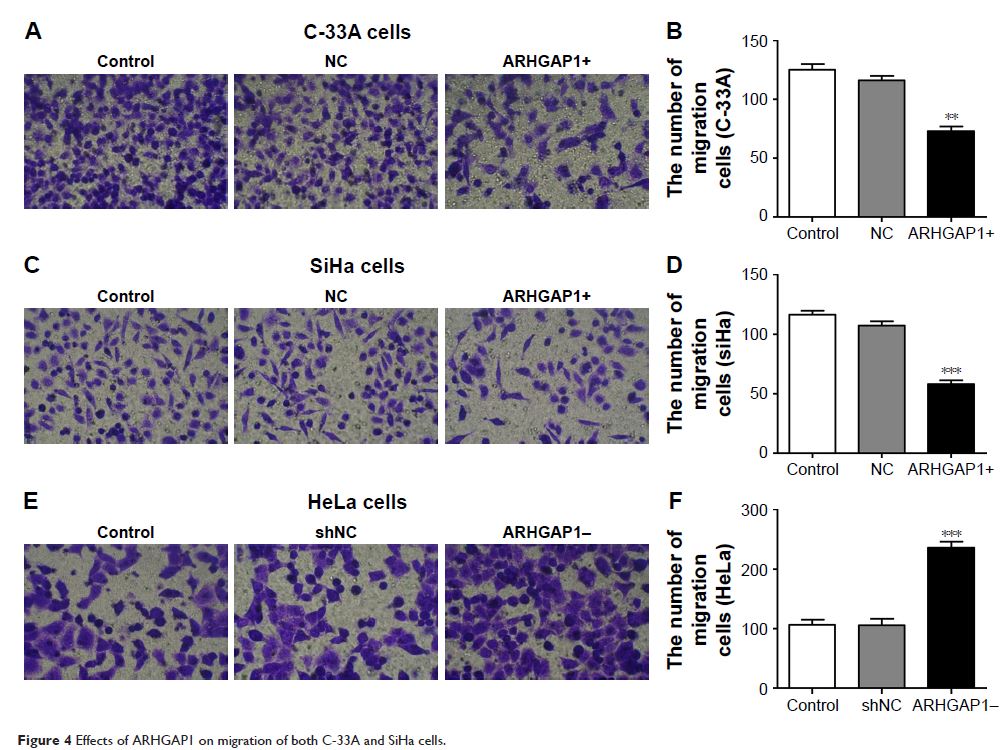
Migration and invasion of C-33A and SiHa cells were suppressed after the
transduction with lenti-ARHGAP1 compared with the controls (n=3, P <0.01). In
addition, several tumor cellular process-related proteins, such as matrix
metallopeptidase 2, zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1, Cyclin B1, twist
family bHLH transcription factor 1 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen, were
all downregulated in ARHGAP1 -overexpressed C-33A and
SiHa cells and proved to be targets of ARHGAP1 . This study indicated that
ARHGAP1 may have a positive function on antitumor activity in the treatment of
cervical cancer.
Keywords: cervical carcinoma, ARHGAP1, tumor
cellular process-related protein