109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

USP21 通过抑制膀胱癌中的 EZH2 泛素化来促进细胞增殖和转移
Authors Chen Y, Zhou B, Chen D
Received 16 October 2016
Accepted for publication 23 November 2016
Published 7 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 681—689
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S124795
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
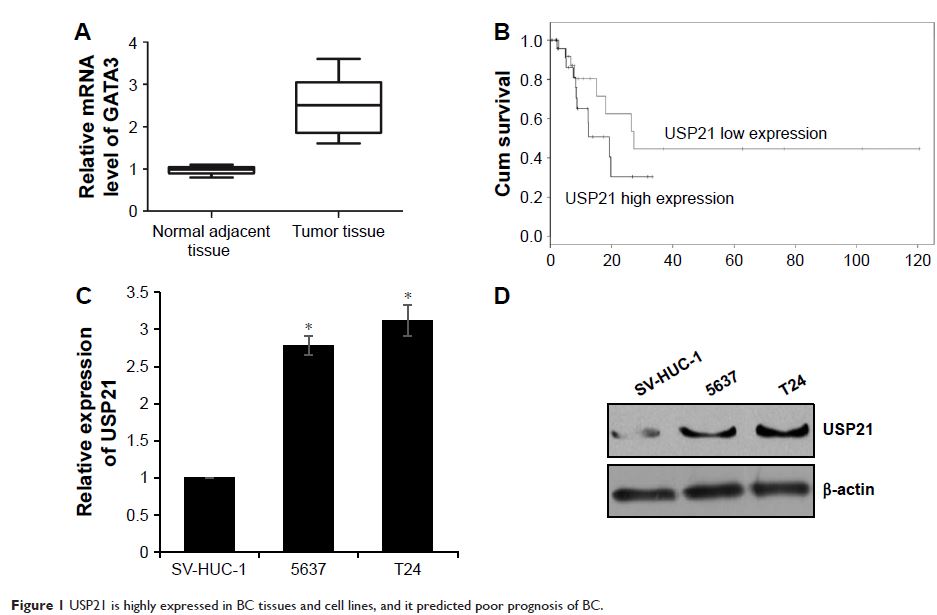
Abstract: Bladder cancer (BC) is the second most common malignant tumor of the
urinary tract in the world. In this study, we found that ubiquitin-specific
protease (USP21) was upregulated in BC and the ectopic expression of USP21 was
closely associated with tumor size and metastasis. Moreover, patients with
higher levels of USP21 had poorer survival rate. Multiple function analysis
such as CCK-8, colony formation, wound healing, and transwell analysis
indicated that USP21 regulated cell proliferation and metastasis in bladder
carcinoma cell lines. We also found that USP21 could facilitate
epithelial–mesenchymal transition. As EZH2 has been reported to promote cell
metastasis in BC, our work identified that USP21 deubiquitinated EZH2 and
stabilized it. Our data demonstrated that USP21 might play a crucial role in
regulating BC progression and could provide a potential therapeutic strategy for
BC.
Keywords: USP21, proliferation, metastasis,
EZH2, EMT