109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
在胃癌细胞中通过 miR-200c 明胶酶刺激 PEG-Pep-PCL 纳米颗粒来增强放射治疗疗效
Authors Cui FB, Liu Q, Li RT, Shen J, Wu PY, Yu LX, Hu WJ, Wu FL, Jiang CP, Yue GF, Qian XP, Jiang XQ, Liu BR
Published Date May 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 2345—2358
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S60874
Received 16 January 2014, Accepted 23 February 2014, Published 13 May 2014
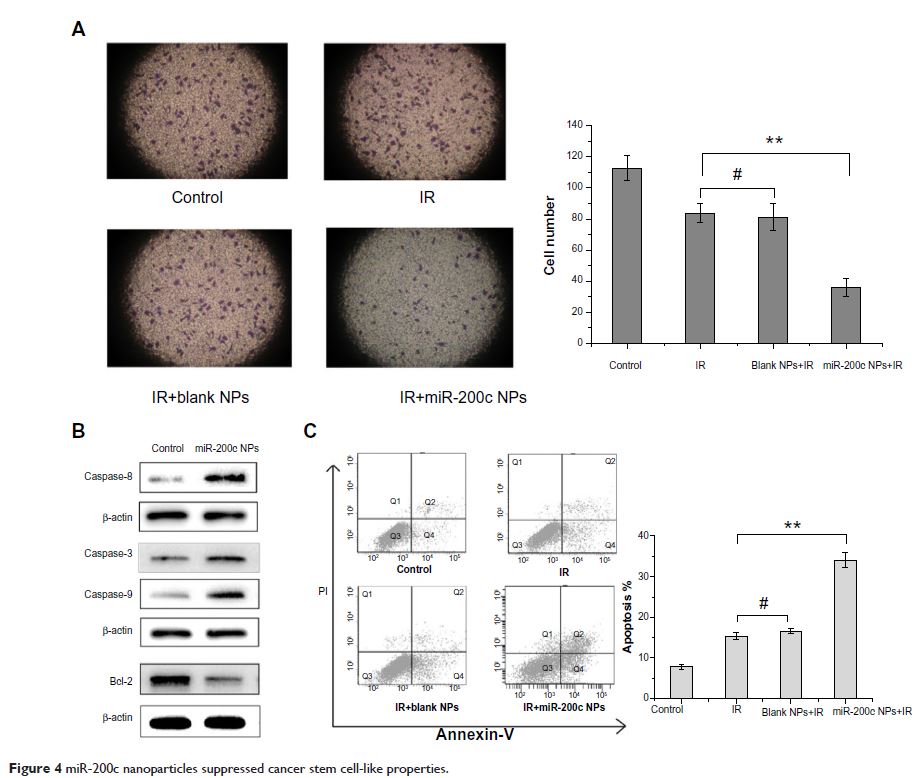
Abstract: Radiotherapy is the main locoregional control modality for many types of unresectable tumors, including gastric cancer. However, many patients fail radiotherapy due to intrinsic radioresistance of cancer cells, which has been found to be strongly associated with cancer stem cell (CSC)-like properties. In this study, we developed a nanoparticle formulation to deliver miR-200c, which is reported to inhibit CSC-like properties, and then evaluated its potential activity as a radiosensitizer. miR-200c nanoparticles significantly augmented radiosensitivity in three gastric cancer cell lines (sensitization enhancement ratio 1.13–1.25), but only slightly in GES-1 cells (1.06). In addition to radioenhancement, miR-200c nanoparticles reduced the expression of CD44, a putative CSC marker, and the percentage of CD44+ BGC823 cells. Meanwhile, other CSC-like properties, including invasiveness and resistance to apoptosis, could be suppressed by miR-200c nanoparticles. CSC-associated radioresistance mechanisms, involving reactive oxygen species levels and DNA repair capacity, were also attenuated. We have demonstrated that miR-200c nanoparticles are an effective radiosensitizer in gastric cancer cells and induce little radiosensitization in normal cells, which suggests that they are as a promising candidate for further preclinical and clinical evaluation.
Keywords: radiosensitizer, miR-200c, gelatinase-stimuli nanoparticles, cancer stem cell-like properties, gastric cancer
Keywords: radiosensitizer, miR-200c, gelatinase-stimuli nanoparticles, cancer stem cell-like properties, gastric cancer