109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过 TAT 靶向固体脂质纳米粒子共同递送紫杉醇 (paclitaxel) 和 TOS-顺铂 (cisplatin),可对宫颈癌产生协同抗肿瘤活性
Authors Liu B, Han L, Liu J, Han S, Chen Z, Jiang L
Received 16 June 2016
Accepted for publication 1 September 2016
Published 31 January 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 955—968
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S115136
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Cervical cancer is a major world health problem for women. Currently,
cancer research focuses on improving therapy for cervical cancer using various
treatment options such as co-delivery of chemotherapeutic agents by
nanocarriers.
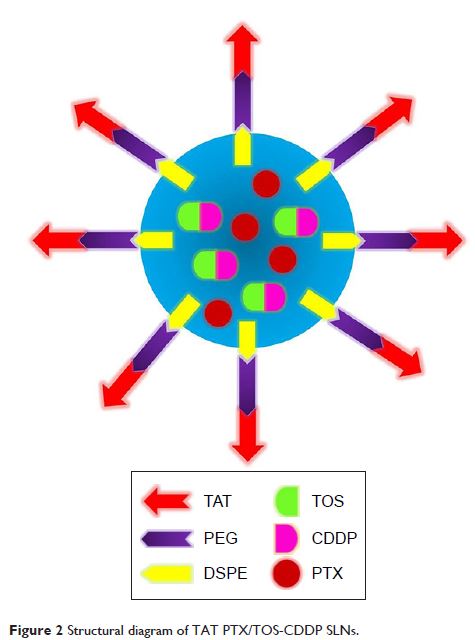
Purpose: The aim of this study was to develop trans-activating
transcriptional activator (TAT)-modified solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) for
co-delivery of paclitaxel (PTX) and α-tocopherol succinate-cisplatin prodrug
(TOS-CDDP) (TAT PTX/TOS-CDDP SLNs) in order to achieve synergistic antitumor
activity against cervical cancer.
Methods: Lipid prodrug of CDDP (TOS-CDDP) and TAT-containing
polyethylene glycol-distearoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine (TAT-PEG-DSPE) were
synthesized. TAT PTX/TOS-CDDP SLNs were prepared by emulsification and solvent
evaporation method. Physicochemical characteristics of SLNs such as size,
morphology, and release profiles were explored. In vitro and in vivo studies
were carried out to assess the efficacy of their antitumor activity in target
cells.
Results: TAT PTX/TOS-CDDP SLNs could be successfully
internalized by HeLa cells and showed a synergistic effect in the suppression
of cervical tumor cell growth. They exhibited high tumor tissue accumulation,
superior antitumor efficiency, and much lower toxicity in vivo.
Conclusion: The present study indicates that the co-delivery
system provides a promising platform as a combination therapy for the treatment
of cervical cancer, and possibly other types of cancer as well.
Keywords: cervical cancer, lipid-based prodrug,
combination therapy, solid lipid nanoparticles, cell-penetrating peptide