108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
肝细胞癌的肝动脉栓塞化疗后,利用中枢和外周静脉内循环肿瘤细胞 — 测量血行传播
Authors Fang ZT, Zhang W, Wang GZ, Zhou B, Yang GW, Qu XD, Liu R, Qian S, Zhu L, Liu LX, Wang JH
Published Date July 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 1311—1318
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S62605
Received 17 February 2014, Accepted 13 May 2014, Published 18 July 2014
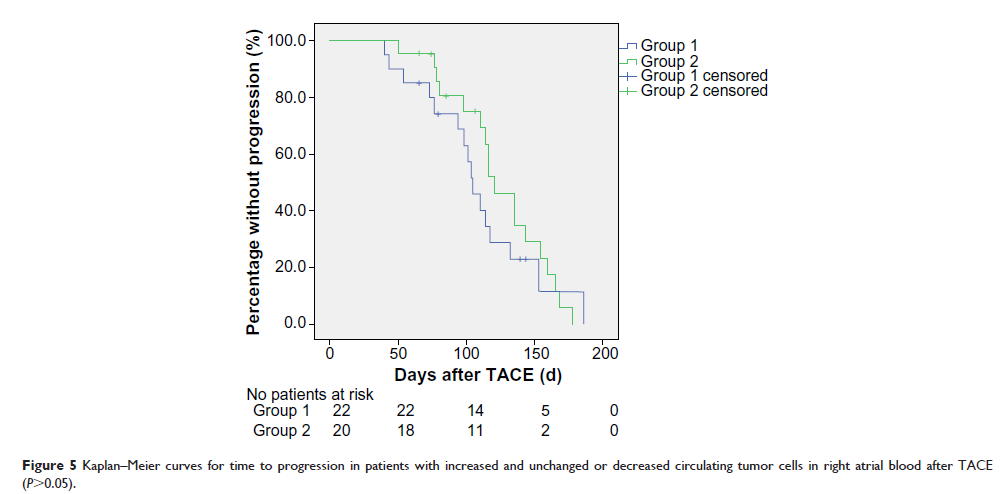
Abstract: The aims of this study were to assess the effect of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) on circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in the peripheral blood and right atrium of patients with HCC and to evaluate whether perioperative shedding of CTCs affects time to progression of HCC. Before and after TACE, peripheral and right atrial blood samples (7.5 mL) were collected from 42 patients with HCC. CTCs were enriched using EpCAM antibody-conjugated magnetic beads. The number of CTCs was 0–30 and 0–54 in peripheral blood before and after TACE, respectively (P =0.166), and 0–65 and 0–98 in the right atrium before and after TACE, respectively (P =0.102). The number of CTCs was significantly different between the two samples both before (P =0.007) and after (P =0.021) TACE. There was no difference in time to progression between patients with and without an increase in the number of CTCs after TACE in either sample (P >0.05 for both). There were more CTCs in right atrial blood than in peripheral blood. The numbers of CTCs in both samples remained unchanged after TACE. Shedding of tumor cells did not affect time to progression of disease in patients with HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, circulating tumor cells, metastasis, positive screening
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, circulating tumor cells, metastasis, positive screening