109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

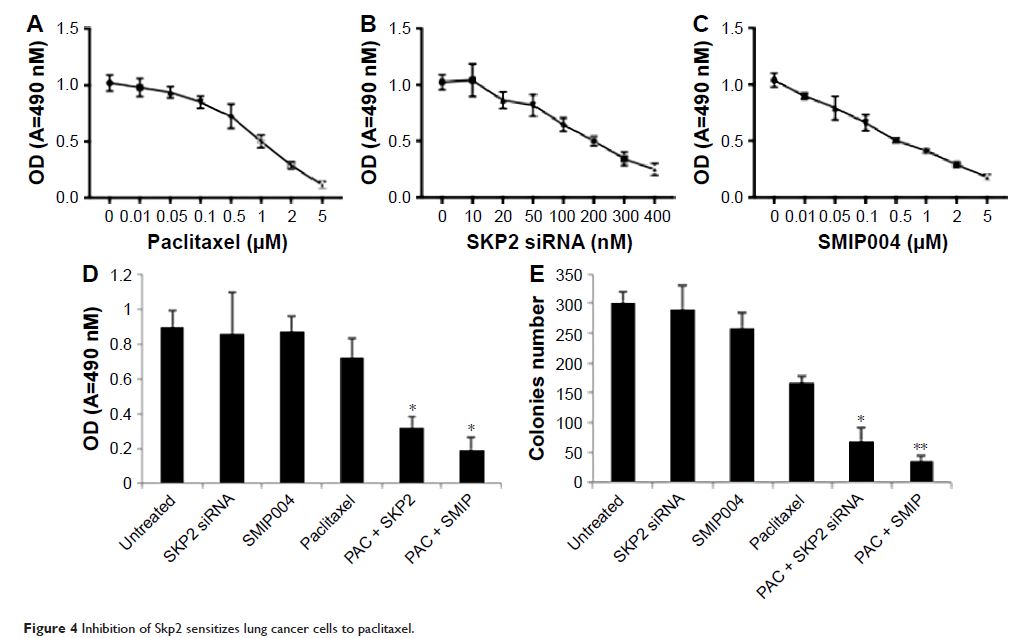
抑制 Skp2 可使肺癌细胞对紫杉醇 (paclitaxel) 敏感
Authors Huang T, Yang L, Wang G, Ding G, Peng B, Wen Y, Wang Z
Received 26 October 2016
Accepted for publication 14 December 2016
Published 18 January 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 439—446
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S125789
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashok Kumar Pandurangan
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Abstract: S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase and
plays an important role in the control of cell cycle progression. Skp2 is
upregulated in several cancers, including lung cancers, but the role of Skp2 in
the tumorigenesis and anticancer drug resistance in human lung cancer remains
to be determined. We report here that Skp2 positively regulated mitotic arrest
deficient 2 (MAD2) expression and that inhibition of Skp2 sensitizes human lung
cancer cells to paclitaxel. Knockdown of Skp2 by small interfering RNA (siRNA)
decreased Mad2 messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels in A549 and NCI-H1975
cells, accompanied with upregulation of p27 but decrease of the phosphorylation
of retinoblastoma (Rb). In contrast, ectopic overexpression of Skp2 increased
Mad2 mRNA and protein levels and phosphorylation of Rb, while it decreased p27.
Pharmacological inhibition of CDK1/2 by flavopiridol or E2F1 with HLM006474 led
to downregulation of Mad2 expression and prevented the increase of Mad2
expression by Skp2. Most importantly, pharmacological inhibition of Skp2
sensitized A549 and NCI-H1299 cells to paclitaxel. Our results demonstrated
that SKP2 positively regulates the gene expression of MAD2 through
p27-CDKs-E2F1 signaling pathway and that inhibition of Skp2 sensitizes A549 and
NCI-H1299 cells to paclitaxel, suggesting that small molecule inhibitors of
Skp2 are potential agents for the treatment of lung cancer with upregulation of
Skp2.
Keywords: SKP2, MAD2, spindle assembly
checkpoint, lung cancer, paclitaxel