109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

N -(3-hydroxymethyl-β-carboline-1-yl-ethyl-2-yl)-L-Phe: 向能够治疗复杂的血栓症和炎症的纳米级抗肿瘤药物的方向发展
Authors Wu JH, Zhao M, Wang YJ, Wang YN, Zhu HM, Zhao SR, Gui L, Zhang XY, Peng SQ
Received 5 October 2016
Accepted for publication 10 November 2016
Published 17 January 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 225—239
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S123919
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Salvatore Bongarzone
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Abstract: It is well documented that the surfaces of cancer cells, activated
platelets and inflammatory cells are rich in P-selectin. N -(3-hydroxymethyl-β-carboline-1-yl-ethyl-2-yl)-l-Phe
(HMCEF) is a P-selectin inhibitor capable of simultaneously inhibiting
thrombosis and inflammation. Based on the knowledge that P-selectin is a common
target for antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and antitumor drugs, the aim of
this study article was to estimate the possibility of HMCEF as a nanoscaled
antitumor drug. Images of transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron
microscopy and atomic force microscopy proved that HMCEF forms nanoparticles
with a diameter of <120 nm that promote delivery in blood circulation.
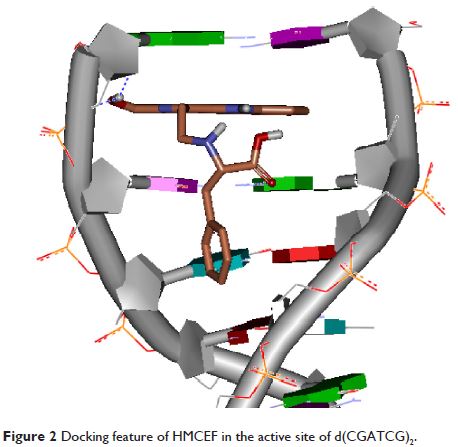
In vitro HMCEF intercalates into calf thymus DNA, cuts off DNA pBR22 and
inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells. In vivo HMCEF dose dependently
(0.2, 2 and 200 nmol/kg per day) slows tumor growth in treated S180 mice,
and has a minimal effective dose of 2 nmol/kg per day. At 200 nmol/kg
per day, HMCEF does not affect the liver and the kidney of the treated S180
mice, and at 20,000 nmol/kg HMCEF does not affect the liver and the kidney
of the treated healthy ICR mice. HMCEF is a promising antitumor drug, which is
characterized by its high safety and efficacy in the prevention of the
complications of thrombosis and inflammation in patients.
Keywords: P-selectin, antitumor, antithrombosis,
anti-inflammation, nanomedicine