109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血小板 - 透明质酸酶响应高密度脂蛋白模拟纳米颗粒用于多级内膜 - 巨噬细胞靶向药物递送和强化的抗动脉粥样硬化治疗
Authors Zhang M, He J, Jiang C, Zhang W, Yang Y, Wang Z, Liu J
Received 9 October 2016
Accepted for publication 30 November 2016
Published 13 January 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 533—558
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S124252
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
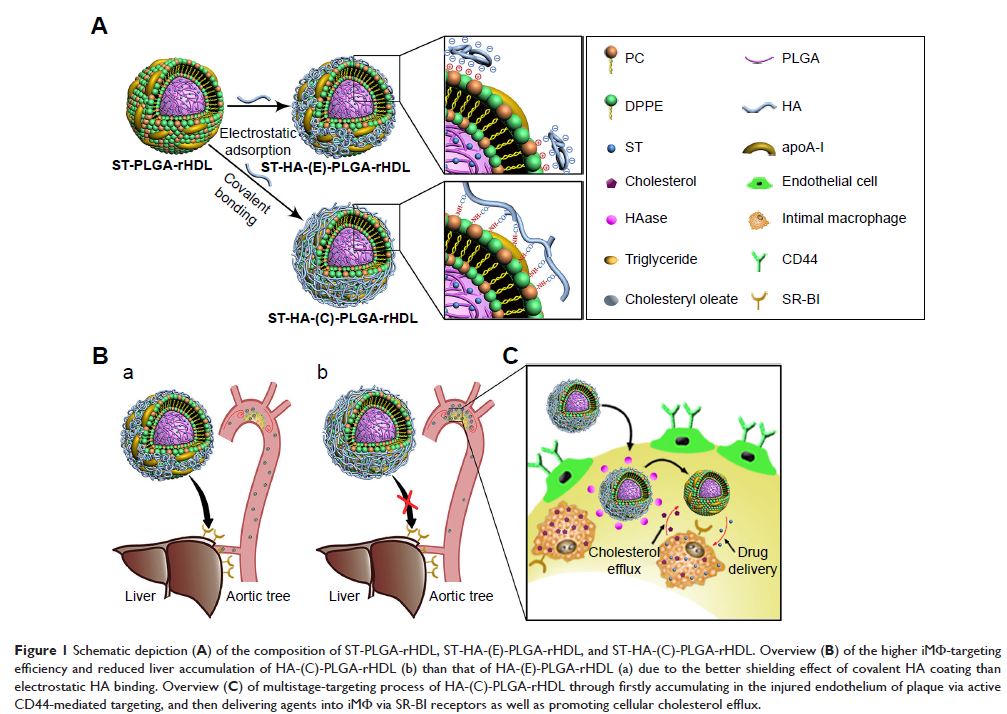
Abstract: Increasing evidence has highlighted the pivotal role that intimal
macrophage (iMΦ) plays in the pathophysiology of atherosclerotic plaques, which
represents an attractive target for atherosclerosis treatment. In this work, to
address the insufficient specificity of conventional reconstituted high-density
lipoprotein (rHDL) for iMΦ and its limited cholesterol efflux ability, we
designed a hyaluronan (HA)-anchored core–shell rHDL. This nanoparticle achieved
efficient iMΦ-targeted drug delivery via a multistage-targeting approach, and
excellent cellular cholesterol removal. It contained a biodegradable poly
(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) core within a lipid bilayer, and
apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) absorbing on the lipid bilayer was covalently
decorated with HA. The covalent HA coating with superior stability and greater
shielding was favorable for not only minimizing the liver uptake but also
facilitating the accumulation of nanoparticles at leaky endothelium
overexpressing CD44 receptors in atherosclerotic plaques. The ultimate iMΦ
homing was achieved via apoA-I after HA coating degraded by hyaluronidase
(HAase) (abundant in atherosclerotic plaque). The multistage-targeting
mechanism was revealed on the established injured endothelium–macrophage
co-culture dynamic system. Upon treatment with HAase in vitro, the nanoparticle
HA-(C)-PLGA-rHDL exhibited a greater cholesterol efflux capacity compared with
conventional rHDL (2.43-fold). Better targeting efficiency toward iMΦ and
attenuated liver accumulation were further proved by results from ex vivo
imaging and iMΦ-specific fluorescence localization. Ultimately,
HA-(C)-PLGA-rHDL loaded with simvastatin realized the most potent anti-atherogenic
efficacies in model animals over other preparations. Thus, the HAase-responsive
HDL-mimetic nanoparticle was shown in this study to be a promising nanocarrier
for anti-atherogenic therapy, in the light of efficient iMΦ-targeted drug
delivery and excellent function of mediating cellular cholesterol efflux.
Keywords: covalent HA coating, rHDL, HAase response, multistage targeting for
intimal macrophage, cholesterol efflux, anti-atherogenic efficacies