109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

老年高危手术患者在胆总管石切除术后出现胆囊收缩的危险因素
Authors Wang T, Luo H, Yan H, Zhang G, Liu W, Tang L
Received 20 October 2016
Accepted for publication 8 December 2016
Published 12 January 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 129—136
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S125139
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Zhi-Ying Wu
Objective: Cholecystolithiasis is a common disease in the elderly patient. The
routine therapy is open or laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In the previous study,
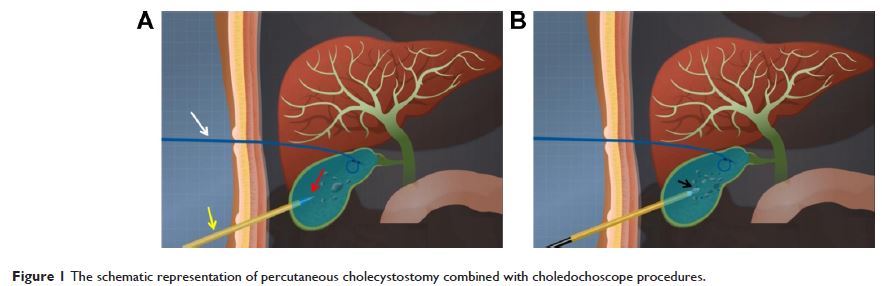
we designed a minimally invasive cholecystolithotomy based on percutaneous
cholecystostomy combined with a choledochoscope (PCCLC) under local anesthesia.
Methods: To investigate the effect of PCCLC on the gallbladder
contractility function, PCCLC and laparoscope combined with a choledochoscope
were compared in this study.
Results: The preoperational age and American Society of
Anesthesiologists (ASA) scores, as well as postoperational lithotrity rate and
common biliary duct stone rate in the PCCLC group, were significantly higher
than the choledochoscope group. However, the pre- and postoperational
gallbladder ejection fraction was not significantly different. Univariable and
multivariable logistic regression analyses indicated that the preoperational
thickness of gallbladder wall (odds ratio [OR]: 0.540; 95% confidence interval
[CI]: 0.317–0.920; P =0.023) and lithotrity (OR:
0.150; 95% CI: 0.023–0.965; P =0.046) were risk factors for
postoperational gallbladder ejection fraction. The area under receiver
operating characteristics curve was 0.714 (P=0.016; 95% CI:
0.553–0.854).
Conclusion: PCCLC strategy should be carried out cautiously.
First, restricted by the diameter of the drainage tube, the PCCLC should be
used only for small gallstones in high-risk surgical patients. Second, the
usage of lithotrity should be strictly limited to avoid undermining the
gallbladder contractility and increasing the risk of secondary common bile duct
stones.
Keywords: cholecystolithotomy, lithotrity,
thickness of gallbladder wall, GBEF, gallbladder motility