109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

共聚物组分对磷酸胆碱胶束性能的影响
Authors Wu Z, Cai M, Cao J, Zhang J, Luo X
Received 26 July 2016
Accepted for publication 8 December 2016
Published 12 January 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 487—500
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S118197
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
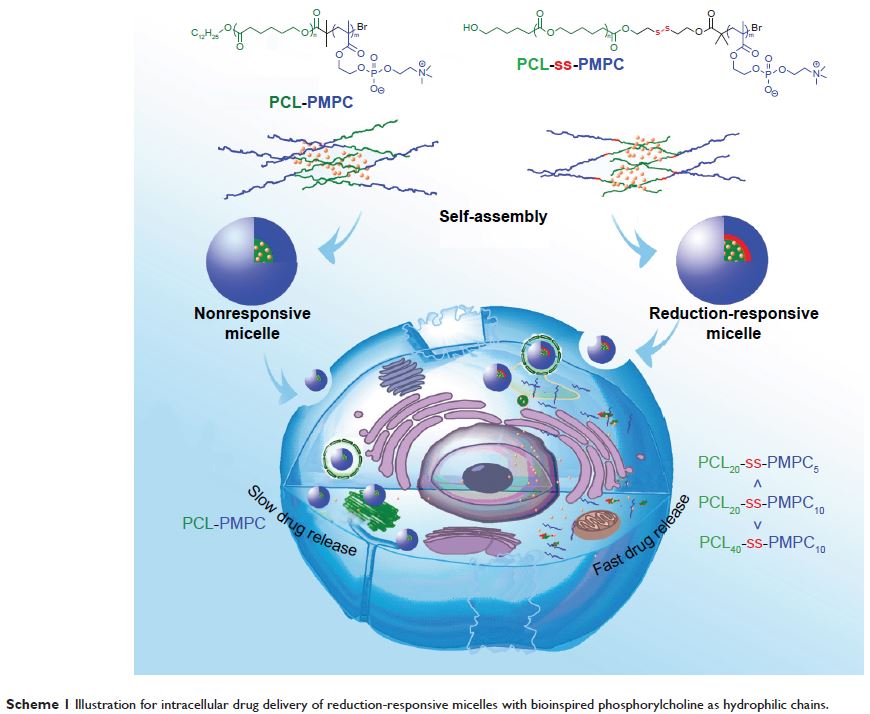
Abstract: Zwitterionic polymers have unique features, such as good compatibility,
and show promise in the application of drug delivery. In this study, the
zwitterionic copolymers, poly(ε-caprolactone)-b-poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl
phosphorylcholine) with disulfide (PCL-ss-PMPC) or
poly(ε-caprolactone)-b-poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) or
without disulfide (PCL-PMPC) and with different block lengths in PCL-ss-PMPC,
were designed. The designed copolymers were obtained by a combination of
ring-opening polymerization and atom transferring radical polymerization. The
crystallization properties of these polymers were investigated. The micelles
were prepared based on the obtained copolymers with zwitterionic
phosphorylcholine as the hydrophilic shell and PCL as the hydrophobic core. The
size distributions of the blank micelles and the doxorubicin (DOX)-loaded
micelles were uniform, and the micelle diameters were <100 nm. In vitro
drug release and intracellular drug release results showed that DOX-loaded
PCL-ss-PMPC micelles could release drugs faster responding to the reduction
condition and the intracellular microenvironment in contrast to PCL-PMPC
micelles. Moreover, in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation revealed that the designed
copolymers possessed low cell toxicity, and the inhibiting effect of DOX-loaded
phosphorylcholine micelles to tumor cells was related to the components of
these copolymers. These results reveal that the reduction-responsive
phosphorylcholine micelles with a suitable ratio of hydrophilic/hydrophobic
units can serve as promising drug carriers.
Keywords: zwitterionic, reduction-sensitive,
disulfide, phosphorylcholine