109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

丙硫氧嘧啶 (Propylthiouracil) 诱导的肝衰竭和人工肝支持系统:病例报告和文献回顾
Authors Wu DB, Chen EQ, Bai L, Tang H
Received 19 September 2016
Accepted for publication 21 November 2016
Published 11 January 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 65—68
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S122611
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Background: Antithyroid drugs carry a potential risk of hepatotoxicity.
Propylthiouracil (PTU) is commonly prescribed for patients with
hyperthyroidism. PTU, however, can induce liver injury, ranging from mild
asymptomatic elevation of aminotransferases to acute liver failure (ALF).
Case presentation: This case reports on a 16-year-old Chinese girl with
hyperthyroidism, who was admitted to our hospital for jaundice, nausea, and
fatigue associated with severe hyperbilirubinemia and coagulopathy. She had
been prescribed PTU 5 months earlier. There was no history of
hypersensitivity to drugs, viral liver diseases, blood transfusion, or surgery.
On the basis of her symptoms and the clinical data, she was diagnosed with
PTU-induced ALF. Due to the limited number of available donor organs for liver
transplantation, she was started on treatment with artificial liver support
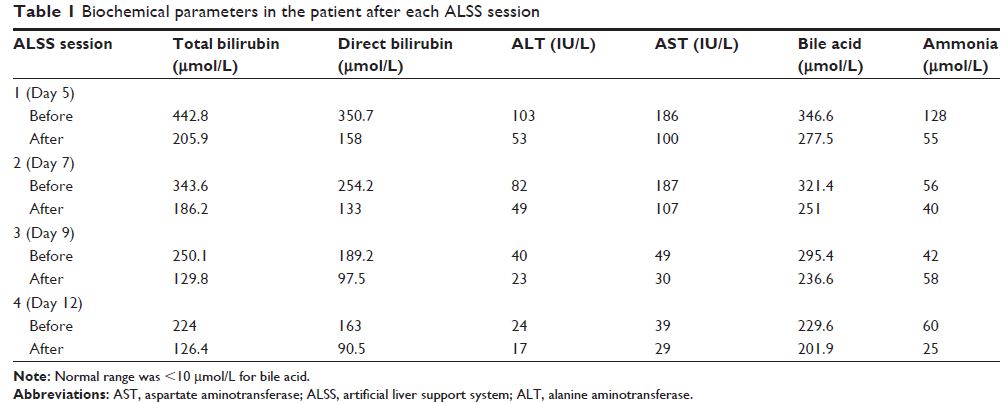
system (ALSS). After four sessions of ALSS, her clinical signs and symptoms
were found to be markedly improved, and she was discharged 25 days after
admission. Four months later, her liver function normalized.
Conclusion: Although PTU-induced liver failure is rare in clinical
practice, liver function should be appropriately monitored during treatment
with PTU. PTU-induced ALF in this patient was successfully managed with an
ALSS, suggesting that the latter may be an alternative to liver
transplantation.
Keywords: propylthiouracil,
liver injury, acute liver failure, artificial liver support systems