109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

协和肽 (Copeptin) 对心力衰竭后全因死亡率的预后作用:一个系统评价和综合分析
Authors Zhang P, Wu X, Li G, Sun H, Shi J
Received 14 October 2016
Accepted for publication 21 November 2016
Published 5 January 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 49—58
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S124689
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Background: As the C-terminal section of vasopressin precursor, copeptin has been
recently suggested as a new prognostic biomarker after heart failure (HF).
Thus, the aim of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of plasma
copeptin level with all-cause mortality in patients with HF.
Methods: Comprehensive strategies were used to search relevant
studies from electronic databases. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and standardized
mean differences (SMDs) together with their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were
calculated. Subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis were performed to find
the potential sources of heterogeneity.
Results: A total of 5,989 participants from 17 prospective
studies were included in this meta-analysis. A significant association was
observed between circulating copeptin levels and risk of all-cause mortality in
patients with HF (categorical copeptin: HR =1.69, 95% CI =1.42–2.01; per
unit copeptin: HR =1.03, 95% CI =1.00–1.07; log unit copeptin: HR =3.26, 95% CI
=0.95–11.25). Pooled SMD showed that copeptin levels were significantly higher
in patients with HF who died during the follow-up period than in survivors (SMD
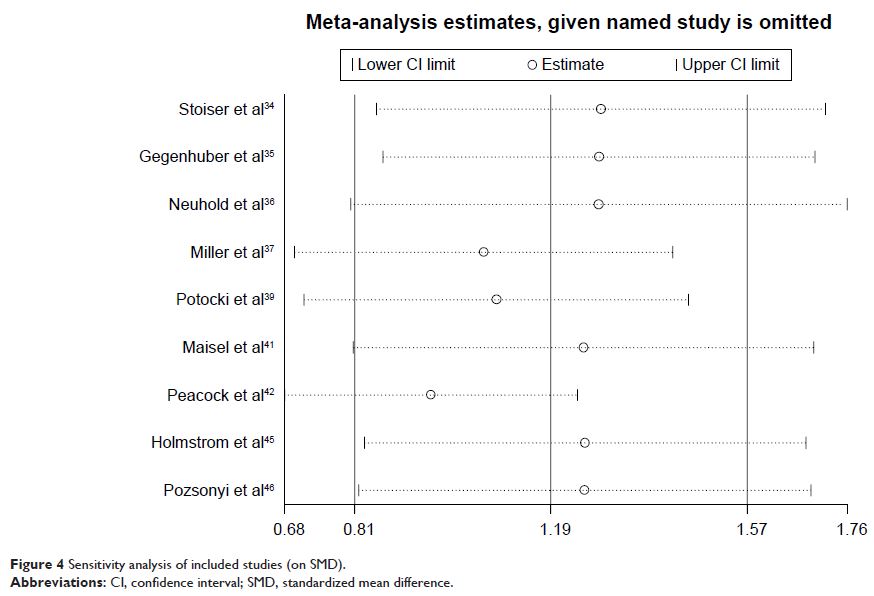
=1.19, 95% CI =0.81–1.57). Subgroup analyses also confirmed this significant
association, while sensitivity analyses indicated that the overall results were
stable.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that circulating copeptin
seemed to be a novel biomarker to provide better prediction of all-cause
mortality in patients with HF.
Keywords: heart failure, copeptin, all-cause
mortality, meta-analysis