109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文已被撤回 - 槲皮素 (Quercetin) - 金纳米颗粒通过在高脂肪饮食喂养的小鼠中调节 TLR4/NF-kB 信号传导和 Nrf2 信号通路来防止代谢性内毒素血症诱导的肾损伤
Authors Xu MX, Wang M, Yang WW
Received 29 June 2016
Accepted for publication 20 September 2016
Published 5 January 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 327—345
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S116010
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
应作者的要求,国际纳米医学期刊的主编决定撤回此文章。
撤稿启事
Abstract: High-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome followed by chronic kidney
disease caused by intestinal endotoxemia have received extensive attention.
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and oxidative
stress-related Nrf2/Keap1 were regarded as the key target points involved in
metabolic inflammation and kidney injury. However, the molecular mechanism of
interaction between TLR4/NF-κB and Nrf2 activation in high-fat diet-induced
renal injury is not absolutely understood. Quercetin, a natural product, has
been reported to possess antitumor and anti-inflammatory effects. In this
regard, this study attempted to prepare poly(d,l-lactide-co -glycolide)-loaded gold
nanoparticles precipitated with quercetin (GQ) to investigate the anti-inflammatory
and anti-oxidative stress effects in high-fat diet-induced kidney failure. For
this study, C57BL/6 mice fed fat-rich fodder were used as the metabolic
syndrome model to evaluate the protective effects of GQ on kidney injury and to
determine whether TLR4/NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways were associated with the
process. Moreover, histological examinations, enzyme-linked immunosorbent
assay, Western blot, and basic blood tests and systemic inflammation-related
indicators were used to investigate the inhibitory effects of GQ and underlying
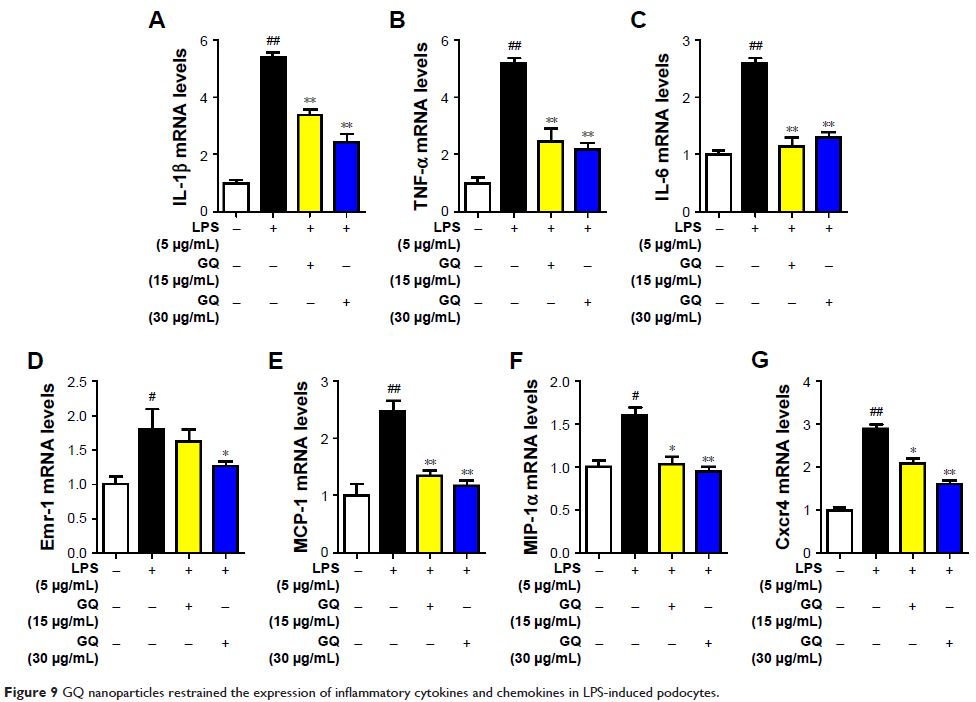
molecular mechanism by which it may reduce renal injury. Of note, podocyte
injury was found to participate in endotoxin-stimulated inflammatory response.
TLR4/NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways were upregulated with high-fat diet intake in
mice, resulting in reduction of superoxide dismutase activity and increase in
superoxide radical, H2O2, malondialdehyde, XO,
XDH, and XO/XDH ratio. In addition, upregulation of TLR4/NF-κB and oxidative
stress by endotoxin were observed in vitro, which were suppressed by GQ
administration, ultimately alleviating podocyte injury. These findings
indicated that GQ could restore the metabolic disorders caused by high-fat
diet, which suppresses insulin resistance, lipid metabolic imbalance, and
proinflammatory cytokine production. Also, it may prevent kidney injury by
inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB and oxidative stress, further increasing superoxide
dismutase activity.
Keywords: gold-quercetin nanoparticles, kidney injury, podocytes, TLR4/NF-κB, Nrf2