109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA CRNDE 作为竞争性内源性 RNA 通过在结肠直肠癌中使 miR-136 海绵化来促进转移和奥沙利铂 (oxaliplatin) 耐药性
Authors Gao H, Song X, Kang T, Yan B, Feng L, Gao L, Ai L, Liu X, Yu J, Li H
Received 1 July 2016
Accepted for publication 20 September 2016
Published 5 January 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 205—216
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S116178
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Min Li
Abstract: Colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed (CRNDE ) is a novel gene recognized
as a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) that is highly elevated in colorectal cancer
and many other solid tumors but its functions on metastasis and oxaliplatin
(OXA) resistance are unknown. In our study, we confirmed the upregulation of CRNDE in both primary specimens from
colorectal cancer patients and colorectal cancer cell lines. Knockdown of CRNDE expression inhibited the migration and
invasion potency of colorectal cancer cells with no effect on cell apoptosis.
Overexpression of CRNDE promoted the migration and invasion
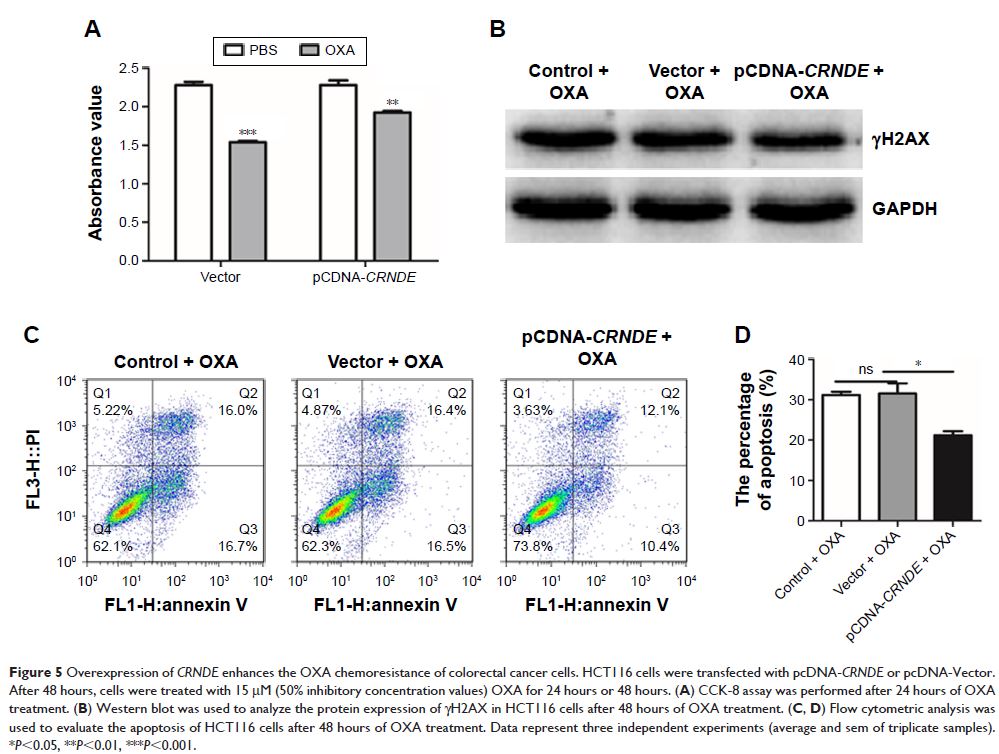
potency of colorectal cancer cells. Furthermore, we found that CRNDE conferred chemoresistance in
colorectal cancer cells. Knockdown of CRNDE with OXA treatment decreased cell
viability and promoted DNA damage and cell apoptosis, while the overexpression
of CRNDE with OXA treatment reduced DNA damage
and cell apoptosis. Further in-depth mechanistic studies revealed that CRNDE functioned as a competing endogenous
RNA for miR-136, led to the de-repression of its endogenous target, E2F
transcription factor 1 (E2F1). Overall, our findings demonstrate that CRNDE functions as a competing endogenous
RNA to promote metastasis and OXA resistance by sponging miR-136 in colorectal
cancer.
Keywords: CRNDE , colorectal
cancer, metastasis, oxaliplatin resistance, miR-136, E2F1