109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

跨文化适应和简版 McGill 疼痛问卷-2 的验证:针对慢性内脏痛患者的中文版
Authors Wang J, Zhang W, Gao M, Zhang S, Tian D, Chen J
Received 12 July 2016
Accepted for publication 31 October 2016
Published 5 January 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 121—128
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S116997
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Schatman
Objective: The
present study aimed to develop a culturally appropriate and functional Standard
Mandarin Chinese translation of the short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire-2
(SF-MPQ-2) and to assess its reliability and validity for characterizing
chronic visceral pain in Chinese patients.
Background: The SF-MPQ-2 has been widely used in studies of pain
epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment, and even pathophysiologic mechanisms to
assess the major symptoms of clinical pain. Previous reports have shown
favorable reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the SF-MPQ-2 in diverse
samples of patients with chronic and acute pain. However, a culturally
appropriate, functional Chinese version of the scale has never been developed.
Methods: Beaton’s guidelines were used for the translation and
back-translation procedures. Patients (n=145) with chronic visceral pain were
recruited to complete the Standard Mandarin Chinese version of the SF-MPQ-2
(SF-MPQ-2-CN), of which 41 were asked to complete the SF-MPQ-2-CN a second
time, 3 days after the initial visit. The test–retest reliability was
quantified using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), and Cronbach’s
alpha was calculated to assess internal consistency. Possible components were
determined by exploratory factor analysis with varimax rotation, and a value of
0.4 was considered requisite for the loading of each factor.
Results: The ICC for subscales ranged from 0.909 to 0.952, and
that of the total scale was 0.927, suggesting excellent reliability and
validity of the SF-MPQ-2-CN. Cronbach’s alpha for subscales ranged from 0.896
to 0.916, and that of the total scale was 0.836 and 0.831 for primary and
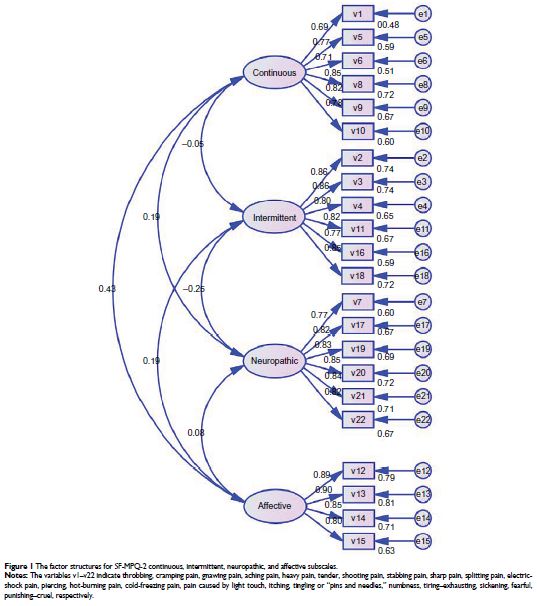
secondary visits, respectively. The factor loading matrix of the SF-MPQ-2-CN
ranged from 0.734 to 0.901 for each of the following subscales: continuous,
intermittent, neuropathic, and affective, revealing four components similar to
the original scale.
Conclusion: The reliability and validity of the SF-MPQ-2-CN scale
are statistically acceptable for the evaluation of Chinese patients with
chronic visceral pain.
Keywords: chronic visceral pain, Chinese version
of short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire-2, exploratory factor analysis,
reliability, validity