109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

低分子量壳聚糖包覆的银纳米颗粒在治疗 MRSA 感染的伤口中很有效
Authors Peng Y, Song C, Yang C, Guo Q, Yao M
Received 14 September 2016
Accepted for publication 16 November 2016
Published 4 January 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 295—304
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S122357
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jiang Yang
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are being widely applied as topical wound
materials; however, accumulated deposition of silver in the liver, spleen, and
other main organs may lead to organ damage and dysfunction. We report here that
low molecular weight chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles (LMWC-AgNPs) are
effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), have better biocompatibility,
and have lower body absorption characteristics when compared with
polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silver nanoparticles (PVP-AgNPs) and silver
nanoparticles without surface stabilizer (uncoated-AgNPs) in a dorsal MRSA
wound infection mouse model. LMWC-AgNPs were synthesized by reducing silver
nitrate with low molecular weight chitosan as a stabilizer and reducing agent,
while PVP-AgNPs were synthesized using polyvinylpyrrolidone as a stabilizer and
ethanol as a reducing agent. AgNPs with different surface stabilizers were
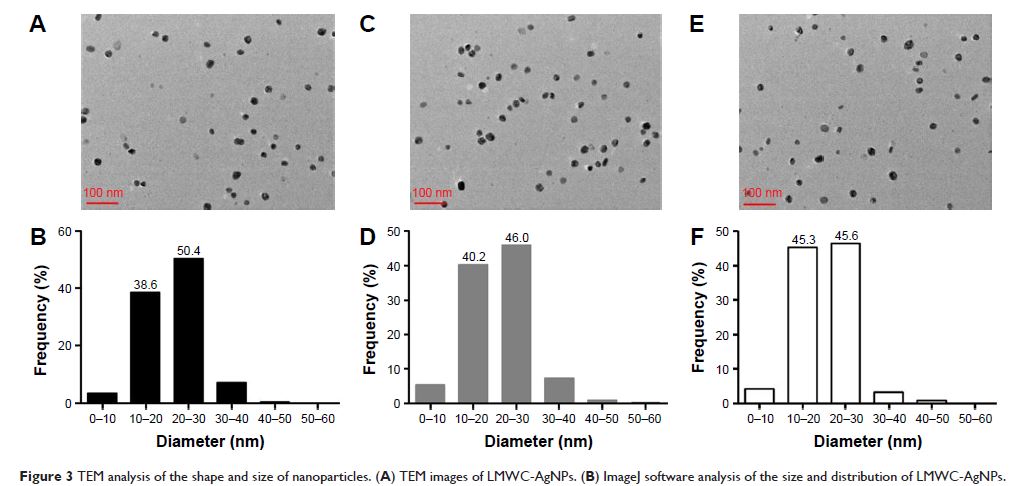
identified by UV-visible absorption spectrometry, and particle size was
determined by transmission electron microscopy. UV-visible absorption spectra
of LMWC-AgNPs, PVP-AgNPs and uncoated-AgNPs were similar and their sizes were
in the range of 10–30 nm. In vitro experiments showed that the three types of
AgNPs had similar MRSA-killing effects, with obvious effect at 4 µg/mL and 100%
effect at 8 µg/mL. Bacteriostatic annulus experiments also showed that all the
three types of AgNPs had similar antibacterial inhibitory effect at 10 µg/mL.
Cell counting kit-8 assay and Hoechst/propidium iodide (PI) staining showed
that LMWC-AgNPs were significantly less toxic to human fibroblasts than
PVP-AgNPs and uncoated-AgNPs. Treatment of mice with MRSA wound infection
demonstrated that the three types of AgNPs effectively controlled MRSA wound
infection and promoted wound healing. After continuous application for 14 days,
LMWC-AgNPs-treated mice showed significantly reduced liver dysfunction as
demonstrated by the reduced alanine aminotransferase and aspartate
aminotransferase levels and liver deposition of silver, in comparison to mice
treated with uncoated-AgNPs or PVP-AgNPs. Our results demonstrated that
LMWC-AgNPs had good anti-MRSA effects, while harboring a better
biocompatibility and lowering the body’s absorption characteristics.
Keywords: silver nanoparticles, LMWC-AgNPs, MRSA, PVP-AgNPs, PVP, biocompatibility