109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用模拟脂蛋白纳米颗粒同时递送抗 miR21 和多种阿霉素 (doxorubicin) 前体药物,产生对抗癌细胞耐药性的协同效应
Authors Rui M, Qu Y, Gao T, Ge Y, Feng C, Xu X
Received 12 September 2016
Accepted for publication 1 December 2016
Published 30 December 2016 Volume 2017:12 Pages 217—237
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S122171
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
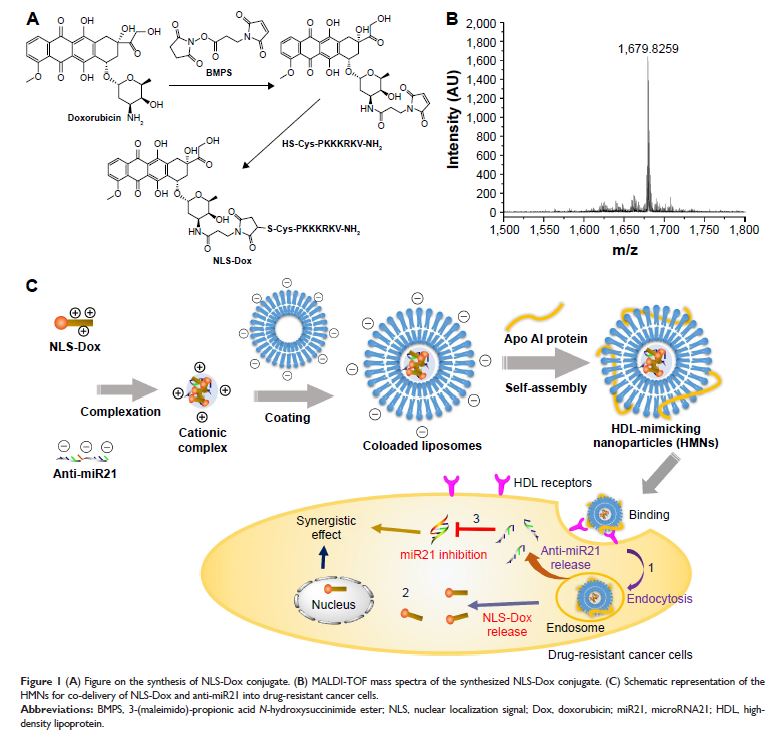
Abstract: The development of drug resistance in cancer cells is one of the major
obstacles to achieving effective chemotherapy. We hypothesized that the
combination of a doxorubicin (Dox) prodrug and microRNA (miR)21 inhibitor might
show synergistic antitumor effects on drug-resistant breast cancer cells. In
this study, we aimed to develop new high-density lipoprotein-mimicking
nanoparticles (HMNs) for coencapsulation and codelivery of this potential
combination. Dox was coupled with a nuclear localization signal (NLS) peptide
to construct a prodrug (NLS-Dox), thereby electrostatically condensing miR21
inhibitor (anti-miR21) to form cationic complexes. The HMNs were formulated by
shielding these complexes with anionic lipids and Apo AI proteins. We have
characterized that the coloaded HMNs had uniformly dispersed distribution,
favorable negatively charged surface, and high coencapsulation efficiency. The
HMN formulation effectively codelivered NLS-Dox and anti-miR21 into
Dox-resistant breast cancer MCF7/ADR cells and wild-type MCF7 cells via a
high-density-lipoprotein receptor-mediated pathway, which facilitated the
escape of Pgp drug efflux. The coloaded HMNs consisting of NLS-Dox/anti-miR21
demonstrated greater cytotoxicity with enhanced intracellular accumulation in
resistant MCF7/ADR cells compared with free Dox solution. The reversal of drug
resistance by coloaded HMNs might be attributed to the suppression of miR21
expression and the related antiapoptosis network. Furthermore, the codelivery
of anti-miR21 and NLS-Dox by HMNs showed synergistic antiproliferative effects
in MCF7/ADR-bearing nude mice, and was more effective in tumor inhibition than
other drug formulations. These data suggested that codelivery of anti-miR21 and
chemotherapeutic agents by HMNs might be a promising strategy for antitumor
therapy, and could restore the drug sensitivity of cancer cells, alter
intracellular drug distribution, and ultimately enhance chemotherapeutic
effects.
Keywords: drug resistance, microRNA21 inhibitor, doxorubicin prodrug, nuclear
localization signal peptide, lipoprotein-mimicking nanoparticles, breast cancer
therapy