109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

黄芩苷 (Baicalin) 纳米脂质体的肺靶向药物递送系统:在兔体内的发展、生物分布,及在患有原位人肺癌的裸鼠中的药效学
Authors Wei Y, Liang J, Zheng X, Pi C, Liu H, Yang H, Zou Y, Ye Y, Zhao L
Received 16 August 2016
Accepted for publication 31 October 2016
Published 29 December 2016 Volume 2017:12 Pages 251—261
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S119895
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Professor Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: The present study aims to develop a kind of novel nanoliposomes for the
lung-targeting delivery system of baicalin as a Chinese medicine monomer.
Baicalin-loaded nanoliposomes were prepared by the effervescent dispersion and
lyophilized techniques. Baicalin-loaded nanoliposomes had an average particle
size of 131.7±11.7 nm with 0.19±0.02 polydispersity index, 82.8%±1.24%
entrapment efficiency and 90.47%±0.93% of yield and sustaining drug release
effect over 24 h and were stable for 12 months at least. In vitro no
hemolytic activity was observed for the experimental drug concentration. After
intravenous administration of baicalin-loaded nanoliposomes to rabbits, drug
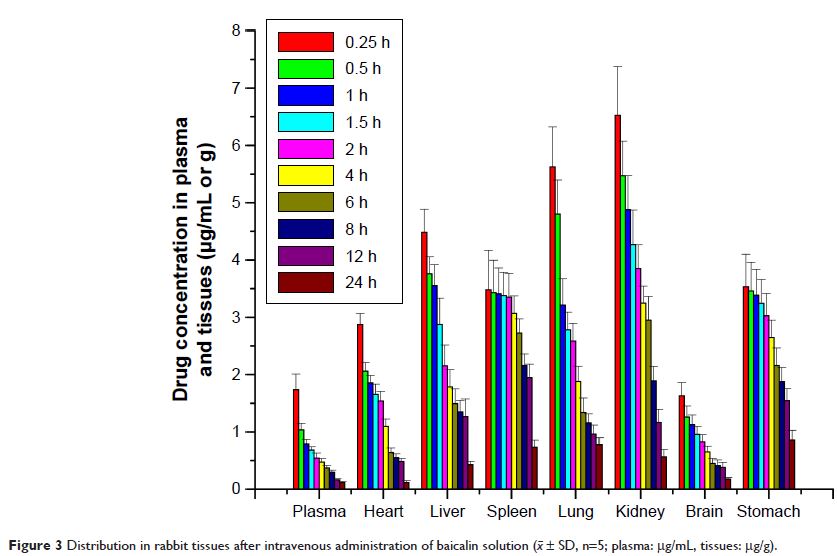
concentration in the lungs was the highest among the tested organs at all
time points and was significantly higher than that of its solution. For the
targeting parameters, the relative intake rate and the ratio of peak
concentration of lung were 4.837 and 2.789, respectively. Compared with plasma,
liver, spleen, and kidney, the ratios of targeting efficacy (Te)liposomes to (Te)injection of
lung were increased by a factor of 14.131, 1.893, 3.357, and 3.470,
respectively. Furthermore, the results showed that the baicalin-loaded
nanoliposomes did not induce lung injury. Importantly, baicalin-loaded
nanoliposomes showed better antitumor therapeutic efficacy in the nude mice
bearing orthotopic human lung cancer with the median survival time of blank
liposomes (11.40±0.16 days), baicalin solution (17.30±0.47 days), and
baicalin-loaded nanoliposomes (25.90±0.53 days). Therefore, the liposome
is a promising drug carrier with an excellent lung-targeting property and
therapeutic effect for the treatment of lung disease, such as lung cancer.
Keywords: liposomes, biodistribution,
lung-targeting drug delivery, cancer therapy, baicalin