109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
长期骑自行车可通过影响白细胞介素-6 和白细胞介素-18 的水平来改善正在接受血液透析的患者的抑郁
长期骑自行车可通过影响白细胞介素-6 和白细胞介素-18 的水平来改善正在接受血液透析的患者的抑郁
Authors Zhao C, Ma H, Yang L, Xiao Y
Received 13 October 2016
Accepted for publication 21 November 2016
Published 28 December 2016 Volume 2017:13 Pages 91—100
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S124630
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Purpose: Hemodialysis patients
with depression have a higher risk of death and hospitalization. Although there
is pharmacological management for the depression of hemodialysis patients, the
adverse effect of the drug limits the use. The nonpharmacological way, bicycle
riding, may be an effective way for the therapy of the depression in
hemodialysis patients. However, the underlying mechanism of this relationship
is still not fully explained, while interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-18
(IL-18) are associated with depression and exercise. Thus, the effects of
bicycle riding on the levels of the interleukin were explored.
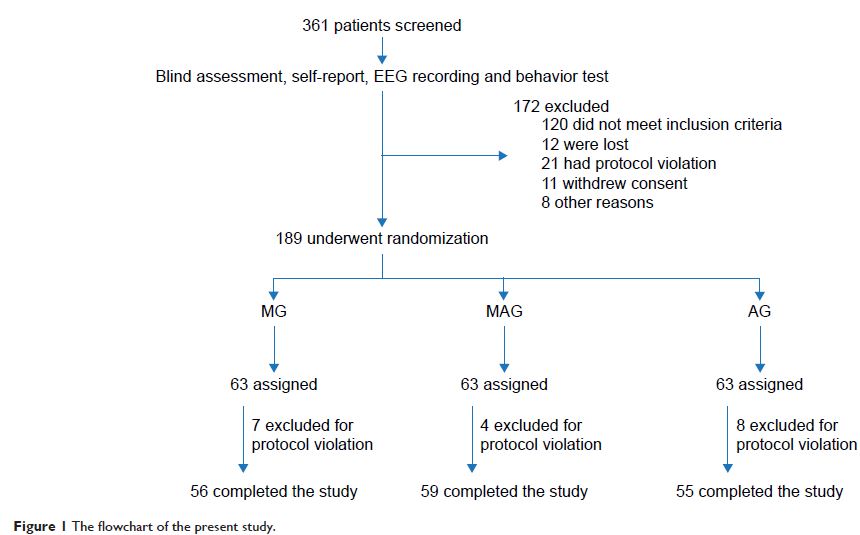
Participants and methods: One hundred and eighty-nine patients with chronic hemodialysis were selected and randomly assigned to three groups of medicine (MG, received 20-mg escitalopram daily), medicine and aerobic exercise (MAG, received 20-mg escitalopram daily and bicycle riding six times weekly), and only aerobic exercise (AG, received 20-mg placebo daily and bicycle riding six times weekly). The whole experiment lasted for 18 weeks. The quality of life (36-Item Short Form Health Survey) and depression severity according to criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , fourth edition [DSM-IV ] were measured before and at the end of this study. The serum levels of IL-6 and IL-18 were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit.
Results: The quality of life was improved and depression severity was reduced significantly in the MAG and AG groups when compared with the MG group (P <0.05). Serum levels of IL-6 and IL-18 were the highest in the MG group, moderate in the MAG group and the lowest in AG group. On the other hand, the serum levels of IL-6 and IL-18 were closely associated with depression scores (P <0.05).
Conclusion: Aerobic exercise improves the quality of life and ameliorates the depression severity of the patients undergoing hemodialysis by affecting the levels of IL-6 and IL-18. Bicycle riding is a potential way for the depression therapy of the patients with chronic hemodialysis.
Participants and methods: One hundred and eighty-nine patients with chronic hemodialysis were selected and randomly assigned to three groups of medicine (MG, received 20-mg escitalopram daily), medicine and aerobic exercise (MAG, received 20-mg escitalopram daily and bicycle riding six times weekly), and only aerobic exercise (AG, received 20-mg placebo daily and bicycle riding six times weekly). The whole experiment lasted for 18 weeks. The quality of life (36-Item Short Form Health Survey) and depression severity according to criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , fourth edition [DSM-IV ] were measured before and at the end of this study. The serum levels of IL-6 and IL-18 were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit.
Results: The quality of life was improved and depression severity was reduced significantly in the MAG and AG groups when compared with the MG group (P <0.05). Serum levels of IL-6 and IL-18 were the highest in the MG group, moderate in the MAG group and the lowest in AG group. On the other hand, the serum levels of IL-6 and IL-18 were closely associated with depression scores (P <0.05).
Conclusion: Aerobic exercise improves the quality of life and ameliorates the depression severity of the patients undergoing hemodialysis by affecting the levels of IL-6 and IL-18. Bicycle riding is a potential way for the depression therapy of the patients with chronic hemodialysis.
Keywords: aerobic exercise, depression, hemodialysis patients