109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

透明质酸改性超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子用于双模态乳腺癌成像和光热治疗
Authors Yang R, Fu C, Fang J, Xu X, Wei X, Tang W, Jiang X, Zhang L
Received 1 September 2016
Accepted for publication 10 November 2016
Published 23 December 2016 Volume 2017:12 Pages 197—206
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S121249
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Professor Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
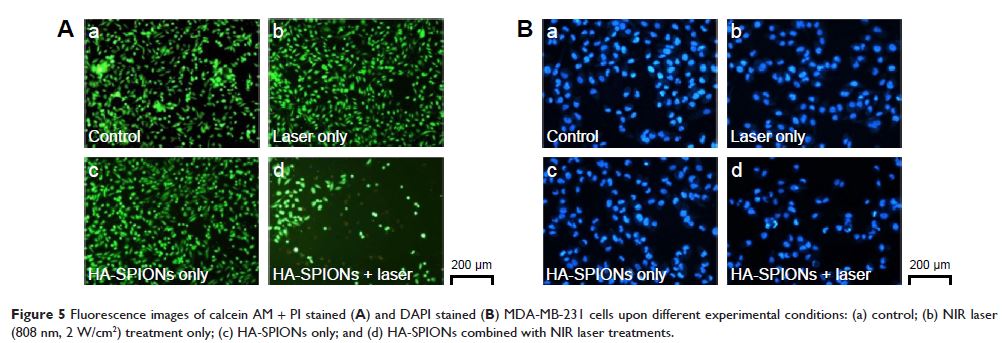
Abstract: Theranostic nanoparticles with both imaging and therapeutic abilities
are highly promising in successful diagnosis and treatment of the most
devastating cancers. In this study, the dual-modal imaging and photothermal
effect of hyaluronan (HA)-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
(HA-SPIONs), which was developed in a previous study, were investigated for
CD44 HA receptor-overexpressing breast cancer in both in vitro and in vivo
experiments. Heat is found to be rapidly generated by near-infrared laser range
irradiation of HA-SPIONs. When incubated with CD44 HA receptor-overexpressing
MDA-MB-231 cells in vitro, HA-SPIONs exhibited significant specific cellular
uptake and specific accumulation confirmed by Prussian blue staining. The in
vitro and in vivo results of magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal
ablation demonstrated that HA-SPIONs exhibited significant negative contrast
enhancement on T2-weighted magnetic resonance
imaging and photothermal effect targeted CD44 HA receptor-overexpressing breast
cancer. All these results indicated that HA-SPIONs have great potential for
effective diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
Keywords: iron
oxide nanoparticles, surface functionalization, bioactive glycosaminoglycan,
magnetic resonance imaging, cellular uptake, breast carcinoma