109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胃癌中 miR-503 表达的降低与血清癌胚抗原呈负相关,同时可作为潜在的预后和诊断生物标志物
Authors Wu D, Cao G, Huang Z, Jin K, Hu H, Yu J, Zeng Y
Received 4 June 2016
Accepted for publication 25 August 2016
Published 23 December 2016 Volume 2017:10 Pages 129—135
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S114303
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Altered expression of miR-503 has been linked to human carcinogenesis.
In this present study, we aimed to detect the potential for miR-503 as a novel
biomarker for gastric cancer (GC) patients.
Materials and methods: The relative mRNA level of miR-503 in serum and tissue
of 68 GC patients and serum of 32 healthy volunteers was determined by
real-time reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
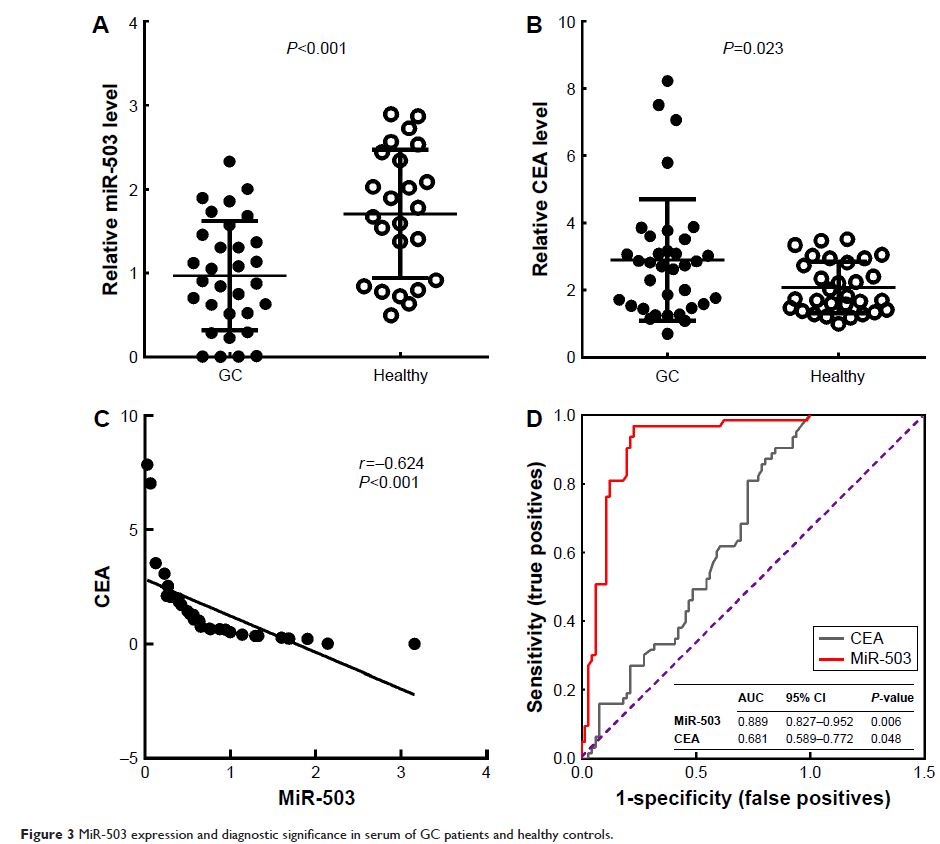
Results: The miR-503 level was significantly lower in the
tissue and serum of GC than their counterparts (all P <0.01).
Downregulation of miR-503 was found to be corrected with more aggressive tumor.
Patients in the high-miR-503 group showed significantly better overall survival
compared to the low-miR-503 group (P =0.021). The serum
miR-503 level in GC was inversely correlated with carcinoembryonic antigen
(CEA) (r =−0.624, P <0.001).
Furthermore, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for
miR-503 discriminating GC patients from healthy individuals was 0.889 (P =0.006), with a sensitivity of
96.8% and a specificity of 79.4%, higher than that of CEA (area under the
receiver operating characteristic curve =0.681, P =0.048).
Conclusion: The present study suggests that the expression level
of miR-503 may serve as prognostic and diagnostic biomarker for GC.
Keywords: microRNA, gastric cancer, diagnosis,
prognosis, biomarker